Administration Guide
The following sections describe how to use the RAC/M Identity Management Console to perform the tasks of operating your IAM service, as well as how to configure and administer the solution.
The various topics are presented in the general order of the Management Console's main menu.
Note
The following instructions assume that you are logged into the RAC/M Identity Management Console with an administrator account with sufficient rights.
See Logging on for the first time for more information.
About operations management
The following sections describe how the RAC/M Identity Administration Console works. The various topics are presented in the general order of the main menu.
RAC/M Identity is designed to operate in a fully automated fashion, with minimal effort required from the operators and administrators. Once configured and fine tuned, the business logic allows the vast majority of processing to be automated.
As the operator, you must ensure that the solution is working properly and your tasks essentially consist of monitoring the indicators, reacting if you receive alerts indicating errors or anomalies, along with investigating and resolving the problems if necessary.
To do this, you will primarily use the Management function in the main menu.
The Management option on the main menu allows you to:
- Review and execute processing sequences
- View logs
- Manage local RAC/M Identity users
- Manage RAC/M Identity profiles
- View audit events
Reviewing and executing sequences
Typically, sequences are set up to run automatically on a schedule and timetable determined during sequence configuration.
Reviewing a sequence
The window displayed when this menu option is opened reflects the results of the last sequence executed. You can also review the detailed results of any other previously run sequence.
To review a sequence execution:
- On the MANAGE menu, click Sequence Executions.
To review the execution of a sequence other than the one displayed, select the sequence to view from the drop-down list.
- In the Sequence to Execute list, select the sequence you want to review.
The last results appear in the LAST RUN DETAILS table. Each module in the sequence is listed along with the number of items processed and the time that it took to process them.
In the Return Code column, the code is 100 indicates that the module was successfully executed. Any other code indicates an error. Point to the question mark icon next to Return Code to view the list of error codes.
If there are any errors during processing, the status of the processing appears in orange or red.
To view error details, you must open the error log file for the module that failed. It is located in the directory that you have identified when configuring the module (see Configuring a Module).
Note
You can view all error logs from the MANAGE menu of the administration console. Choose Log Files to access the log viewing page.
Running Sequences Manually
Generally, a sequence is scheduled to run automatically (see Configuring a Sequence), but you may need to run it manually, especially when first testing new sequences.
To run a sequence manually:
- From the MANAGE menu, click Sequence Executions.

From the Sequence to Execute list, select the sequence you want to run manually.
To restart the processing from the beginning, click the check box Restart from beginning.
Click Start.
You can see the progress of each module as they run. You can review the results at the end.
Stopping and restarting a sequence
You can stop a running sequence by clicking on the Stop button and restart it by clicking on the Start button.
Viewing log files
To view the logs:
On the MANAGE menu, click Logs Files.
From the list, select the file you wish to view.
You can view the contents of the logs in raw format by clicking on the icon located at the top right of the main screen.
Note
The content of the error logs is very technical and is mainly used to investigate the cause of problems. The logs are useful to OKIOK's technical support team as well as to integrators and technical experts of the solution.
Managing local users
There are two types of RAC/M user accounts: local users that are typically only used to initially configure and setup RAC/M Identity and federated user accounts that are used on a day-to-day basis by end users, operators, managers, approvers, reviewers, etc. to perform IAM operations and to manage an operational RAC/M Identity implementation.
Local accounts are created from the administrative console and are authenticated using the built-in password database. There should normally only be a very small number of local accounts, ideally only one. Local accounts are normally only used for the initial setup and configuration of RAC/M Identity.
Federated accounts do not need to be created manually because they are imported from an enterprise directory such as Active Directory or Entra ID. Federated accounts are authenticated using an external authentication mechanism such as Active Directory or a SAML authentication provider and assigned by business rules to the proper RAC/M Identity profile based on their responsibilities.
To create or edit a local user:
- On the MANAGE menu, click on RAC/M Users.
- At the top right of the page, click on the
button.
- Under Details, enter the required information as follows:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Username | In the text box, enter the name that will be used to log in to RAC/M Identity. |
| Full Name | In the text box, enter the user's full name. |
| RAC/M Profile | From the list, select the profile you wish to assign to the user. This determines which menus and functions the user will have access to. If the desired profile is not listed, you can create it. |
| Associated Identity | This is used to associate an identity with this internal user. If necessary, select an identity from the list to associate with the new user. The user will then be able to authenticate using the ID and password of the associated identity instead of the internal ID and password. |
| New Password | Enter the password that will be used to log into RAC/M Identity. |
| Password Confirmation | Enter the password that will be used to log in to RAC/M Identity. |
- Click Save.
Important
Although this password is only used for the initial setup of RAC/M Identity, it is important that you choose a high quality password to ensure sufficient protection during the installation and setup process.
It will be possible (and recommended) to disable the use of built-in passwords once an authentication provider is configured.
To generate or revoke an API Key
API keys are used to authenticate to the RAC/M Identity servers when using Web services. Once generated they must copied and pasted where they will be used.
To generate an API key:
1- Click on the Generate button.
To regenrate an API key:
1- Click on the Regenerate button.
To revoke an API key:
1- Click on the Revoke button and confirm when requested.
Important
API keys are sensitive cryptographic material that must be protected to prevent unauthorized access to the RAC/M Identity Web services. You must use utmost care to prevent the keys from being compromised.
Managing RAC/M Identity profiles
In RAC/M Identity, profiles let you define which menus and functionalities users will have access to. This is useful to limit what certain users can see and do within the management console based on their responsibilities.
To create a RAC/M Identity profile:
- On the MANAGE menu, click RAC/M Profiles.
- Click the Create new button
.
- In the RAC/M Profile text box, type a name for the profile.
- In the Landing Page list, select the page that the users will see after logging on.
| Landing page | Description |
|---|---|
| Dashboard | The main landing page with a full dashboard with graphical indicators. This is the standard landing page for using the administrative console for operators and administrators of RAC/M Identity. |
| Self-Service | This is the landing page normally used for end-users, managers, approvers and reviewers who only need to perform IAM tasks such as issuing and approving requests or performing access review campaigns, but do not need access to RAC/M Identity management functions. |
- Under Items, select the check boxes corresponding to the permissions you want to grant to the profile.
- Click Save.
Note
Keep in mind that selections and changes apply to all users with this profile.
See Also
Viewing the audit trail
The audit trail displays, in chronological order, a detailed history of all requests, decisions and actions taken by RAC/M Identity whether initiated by the management console, the self-service portal, automated processing, web APIs or any other way.

The audit trail provides complete traceability of all events that may affect access and allows the determination of the accesses held by an identity at a given time.
The audit log is very detailed and therefore very large. To facilitate analysis and searches for specific events, elaborate filtering functions are available.
You can filter by date by clicking on the calendar icon at the top right of the filter and select or deselect the specific event categories or events you want to retain or remove.
Events that add rights are shown with a green circle, events that remove rights are shown with a red circle, while events related to automated processing are shown with a blue circle.
To view the audit log:
- On the MANAGE menu, click Audits. The main screen displays the latest audit events.
- Determine the date range you want to analyze and select or deselect the events you want to retain or eliminate for analysis.
The screen is split in two sections, one is the Activity Feed and the other section is the Filter

Activity Feed
The section on the left, named Activity Feed, presents a timeline starting from the most recent record. Each of these records offers information about the event as well as a contextual tooltip about the entities involved in that record. Some of these records may have additional information that can be displayed by pressing the drop down icon .
| Icons | Description |
|---|---|
| Expands the section to view more information in relation to a specific audit record. | |
| Reloads the audit list with the latest records in the database. |
If the records are related to sequence executions, icons help to quickly understand the event:
| Sequence Icons | Description |
|---|---|
| Start of sequence | |
| End of sequence | |
| Start of module | |
| End of module |
Filters
The section on the right represents the filters that can be used to reduce the information that is displayed on the left. At the top of this section, two icons help you with the filters.
| Filter Icons | Description |
|---|---|
| Represents the number of filters that have been selected. | |
| Allows for selection of a start and end date. |
The search box helps you find the filters you are interested in and makes it easier to select them. If you do a search with this filter box, you have two options.
- Select all search results. Allows you to select all visible items in the filter list.
- Add the selected items to the current filter. Allows you to make selections from this list and, when you press Apply, these selections will be added to the previous selection. If you don't choose this option, when you press Apply, the previously selected filters will be replaced by the ones chosen before you pressed this button.
When selections are made, click Apply to filter the list on the left.
Audit Sidebar
When you open an entity detailed panel, the audit sidebar may be present which is identified by the label Activity Feed. If it is the case, it will look like this:

Click on the Activity Feed sidebar to expand it. Once opened, the left sidebar looks like this:

The Activity Feed sidebar functions like the Dedicated Panel described above with some exceptions:
- The sidebar shows the Activity Feed when initially displayed. If you click on the upper right filter icon, the sidebar will transition to the filter selection.
- In the filter context, you can make selections, and click on the Apply button. When the button is clicked, the context changes back to the Activity Feed with the selected filter affecting the list.
Audit log files
User actions which trigger audits are recorded by a special "AUDIT" recorder. Actions which trigger batch audits are not logged. These actions are usually performed by the system.
Recorded audits can be sent to a SIEM solution by modifying the log4j configuration. Here's an example that can be added to the configuration of the log4j2.xml file to create a file containing audit logs only:
<Configuration>
<Appenders>
...
<RollingFile name="Audit" fileName="logs/audits.log" filePattern="logs/audits.log.%i">
<PatternLayout>
<Pattern>%d [%X{request_id}] [%X{login}] [%X{user}] [%X{client_ip}] [%-5p] [%t] [%c] %x- %m%n</Pattern>
</PatternLayout>
<Policies>
<SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy size="10MB"/>
</Policies>
<DefaultRolloverStrategy max="10"/>
</RollingFile>
</Appenders>
<Loggers>
...
<logger name="AUDIT" level="info" additivity="false">
<appenderRef ref="console"/>
<appenderRef ref="Audit"/>
...
</logger>
</Loggers>
</Configuration>See also
Documentation for the Log4j library configuration can be found here: Log4j Configuration
About People
This section presents how to manage Persons, Identities and Accounts in RAC/M Identity
For this purpose, you will use the People function in the main menu.
We use the term People to refer to the human aspect in RAC/M Identity. In this context, Persons, Identities and Accounts are related to People.
The People option in the main menu allows you to:
- View, edit, add and remove Persons
- Match identities to Persons
- View, edit, add and remove Identities
- Match Accounts to Identities
The Approve Matching and Match Audits options are deprecated and should not be used.
Persons
Persons are physical persons who interact with information systems. They must be managed by the RAC/M Identity repository.
Identities
Identities are the business relations a person has with the organization. A person may have multiple simultaneous identities.
Example
Take Chantal St-Germain for example. She works at St-Jude hospital. She is both a practicing physician and a researcher. As such, two entries were originally created for her in two separate identity sources the database for physicians and the database for external university researchers.

These two identities give her access to different applications, via accounts and logical accesses, physical keys, and areas within the hospital.
The information found in these identity sources:
- In the first identity source (which identifies her as a practicing physician), her surname was spelled “Saint-Germain".
- In the second identity source (which identifies her as a researcher), her surname was spelled “St-Germain" and the letter “e” is missing from her surname.
Even though they were not entered the same way in the sources, in RAC/M Identity, they are linked to the same person and considered as Chantale St-Germain.
Because RAC/M Identity links these two identities to a single person, there is no need to standardize the different identities that have been created in the original systems. If you create a new identity for Chantale, it will also be linked to the person.
Therefore, when her research project will finish, her identity as researcher will become inactive and the corresponding accesses will be revoked. But all accounts and logical accesses to assets, required to work as a physician, will remain active and valid.
Importing Persons and Identities
This section outlines the steps you need to take to import identity and access data, such as people, identities, accesses, and entitlements, into RAC/M Identity to perform identity management analysis and processing.
To import persons and identities:
- Review the IdentitiesImport collector that will import the data into the staging table. If the data is imported from a CSV file, the primitive used will be ModuleCopyCSVToTable. If the data is imported using an ICF connector, the primitive used will be ModuleICFImport Data.
- If required, use a formatter and additional modules if the source data needs to be adapted to fit the RAC/M table format.
- Review the IdentificationCopy module that will copy the data from the staging table into the RAC/M repository. The ready-made module is ModuleCopyColumnsAndInserts.
- Review the Imports and Copies blocks to run, among other objects, the IdentitiesImport collector and the IdentificationCopy module.
- Review the imports sequence to make sure that it contains the Imports and Copies blocks.
You can then execute this basic sequence to import data.
See also
Adding Persons and Identities Manually
Normally, people (persons) and their business relationships (identities) are added to RAC/M Identity by importing data from identity sources (see About analyzing data). However, you may need to manually create an identity for a person, say a consultant.
Note
Since there are no autoritative sources for Persons, Identities are usually automatically converted to Persons by the business logic when they are first imported. This virtually eliminates the need to manually create people in RAC/M Identity.
This rare case should only occur if a person needs access to your systems but there is no identity source or way to import and convert one.
See also Converting an Identity to a Person
Adding a person
To add a Person:
On the Menu Bar, click PEOPLE> Persons.
At the top right of the page, click the
button.
Enter the required information as follows: Under Details:
Last Name, Middle Name, First Name
Type all information pertaining to the person. The content of the Last Name text box will appear in the first column of the RAC/M identity table. The first name will appear in the third column.

Maiden Name, Full Name, Social Security Number
This information is not mandatory but can be useful to differentiate people with the same name.
Note
Be sure to comply with your policies and applicable privacy laws regarding the capture and use of user information such as date of birth and social security number. In most jurisdictions, this information is considered highly confidential and its use is governed by laws and regulations.
Date of Birth, Email, Optional Email
Date of birth opens a calendar from which you select the day, month, and year of the person's birth date.
At the bottom of the page, click the Save button. Continue entering the information and save the changes by clicking the Update button. Under More
Address
In the text box, type the address of the person.

Home Phone Number, Additional Phone Number, Cellular Phone Number, Pager Number
This information is not mandatory but can be useful if a person needs to be reached outside the organization.
Creation Date and Last Modified
These boxes indicate the creation date of the entry in RAC/M and when it was last modified. This is useful when actions need to be taken when a person no longer works with the organization or his/her status has changed.
Under Additional Information:
Languages
In the text box, type the person's preferred language for communications.
It is possible to enter a specific locale, for example "en_US" for American English. The chosen language is used for emails and the locale is used for displaying dates. Refer to Locale configuration for more information.

Identifier1 and Identifier2
These text boxes can be used to hold additional information that can be useful to the business logic in sequences, role modeling or access reviews.
Extended Attributes
This section displays the extended attributes that have been attached to the identity object. They may be used to hold comma separated list of values that are relevant to manage access to your information systems such as certifications, training, qualifications, interests, etc.
Click the Update button.
The person is added to RAC/M Identity. If the person is not associated with an identity, its Effective status is automatically set to “Terminated.”
Note
The list of identities associated to the person, located at the bottom of the page, will remain empty until you match the person to an identity in the Identity Matching or Identities page.
Adding an Identity
Note
Identities are typically imported from identity sources such as HR systems, student databases, or intern and contractor registries. This virtually eliminates the need to manually create Identities in RAC/M Identity.
This rare case should only occur if someone needs access to your systems but there is no source of identity or way to import it.
To add an identity:
On the Menu Bar, click PEOPLE> Identities.
At the top right of the page, click the
button.
Enter the required information as follows: Under Details:
Last Name, Middle Name, First Name
Type all information pertaining to the identity. The content of the Last Name text box will appear in the first column of the RAC/M identity table. The first name will appear in the third column.

Employee Number, Source, Birth Date, and Email
In the text box, type the number of the employee; it is possible that there is no number if, for example, the person is an external consultant. The Birth Date opens a calendar from which you select the day, month, and year of the person's birth date. Type the person's email.
In the Source list, select the source where the identity information came from. This may be one of the existing sources (for example, when adding historical data) or you may have to create a new source.
Note
Be sure to comply with your policies and applicable privacy laws regarding the capture and use of user information such as date of birth. In most jurisdictions, this information is considered highly confidential and its use is governed by laws and regulations.
Associated Person
In the list, type the first or last name of the person and elect the person for which you are creating this new identity. If the person’s status was “Terminated”, it will become “Active” after you save the identity if it is active.
At the bottom of the page, click the Save button. Under Employment:
Organization and Department
In the Organization list, select the organization for which the person works under this new identity. In the Department list, select an existing department in which the person will be working as this new identity or type the name of the new department if one has been created for the identities that will work there.

Title, Work Location, Employment Status, and Employment Type
Open each list and select the items that apply to the new identity.
Cost Center, Hire Date, and Termination Date
In the Cost Center text box, enter the name of the department in charge of the person's payroll. The Hire Date opens a calendar where you select the day, month and year the person started working under this new identity. The End Date can be used to indicate the end date of employment to initiate the access revocation process.
Tip
It is a good practice to include an end date for contractors and external users to ensure that accesses are automatically revoked when their contract ends.
Supervisor, Reviewer, Approver Group and Group to be notified during provisioning
In each of the lists, type the first few letters of the name or click on the arrow to open the list and select the supervisors, the people responsible for reviewing and certifying access and the delegation groups that must approve access requests.
Under Additional Information:
Address, Country, Telephone, Mobile Type, Occupation, and Language
In each text box, type the required information.

Identifiers
These text boxes can be used to contain additional pieces of information such as identifiers that may be useful for business logic in sequences, role modeling or access reviews.
Account names
You can use these text fields to enter the basic access account names associated with an identity. For example, these account names can be used by business logic to facilitate account matching or to create accounts in target systems. These fields are typically populated automatically by the business logic.
Tip
For example, identifier and Account names fields can be used to enter accounts or account nomenclatures different from the primary account that must be used for certain legacy environments such as IBM mainframes. In this way the business logic will be able to create accounts according to arbitrary nomenclatures.
Extras
The extra information help you identify the identity when matching persons to them. You can enter any value in these text boxes.
Under Business Functions and Extended Attributes:
Business Function, Start Date, and End Date
In the Business Function list, type the first few letters of the business function that corresponds to a responsibility assigned to an identity and select it from the list or type the name of the business function to assign. The Start Date opens a calendar from which you select the day, month, and year when the person started, or will start, this function. In the End Date field, enter the date when this business function ends. If you need to add a business function, click the
button.
See also
Extended Attributes
This section displays the extended attributes that have been attached to the Identity object. They can be used to contain a comma-separated list of values that are relevant to managing access to your information systems, such as certifications, education, qualifications, interests, etc.
Click Update.
The identity is added.
Note
The list of accounts associated to the person (located at the bottom of the page) will remain empty until accounts are matched, either automatically or manually in the Account Matching page.
Merging Persons
If you realize that 2 or more persons created in RAC/M Identity correspond to the same physical person, you can merge them to correct the repository.
To merge people:
On the Menu Bar, click PEOPLE> Persons.
In the Search text box, type the name of the multiple entries.
In the list, select the Merge check box next to the entries to merge.

Click the Merge button located at the bottom of the page.
The Person Merge page opens, displaying the list of persons you selected.
In the Target column, select the person you want to keep. This will be the person that will remain and who will now combine all the information.
Note
The person selected as the target of the merge will be the authoritative source of information on that person. The other person’s information will be discarded except for associated identities which will be copied.
Important
The merge cannot be undone. The next time data is imported the information will not be duplicated again.
Click the Merge button.
The persons have been merged.
Converting an Identity to a Person
If you have an orphan identity, that is, an identity that is not associated to a person, and there is no one to whom you can assign it, you can create a person based on that identity.
Note
In general, identities are automatically converted to persons by the business logic when identities are initially imported from authoritative sources. This manual procedure is only used in the rare case where the business logic cannot perform the conversion.
To convert an identity to a person:
On the Menu Bar, click PEOPLE> Identity Matching. The Account Matching page opens.

In the list on the left, select the identity for which you want to create a person.
Note
If the list is long, in the text box, type a few letters of the identity you are looking for and click the magnifying glass button.
Click the Create Person button.
The Person page opens and the information already contained in the identity is automatically entered. You can complete the person's record with the available information if necessary.
Click Save.
The new person is created and the status is set to “Active”.
Note
The identity from which you created the person is automatically added to the list of identities located at the bottom of the page.
Matching Identities to People
If the system was not able to automatically match some identities because there are no unique keys (see Determining Unique Identifiers), you will have to manually match them.
To match an identity to a person:
On the Menu Bar, click PEOPLE> Identity Matching. The Identity Matching page opens.

In the list on the left, select the identity to which you want to match a person and click the Create Person button. At the top of the list on the left, in the text box, type some letters of the name of the person you are looking for and click the magnifying glass button. A list of people identified by the selected matching algorithms is displayed in the right section.
Select the person you want.
At the bottom of the page, click the Match button.
The identity and the person have been matched. The identity now appears in the list at the bottom of the person's details page.
Note
If the list is empty, you can enter a few letters of the name of the person you are looking for in the search bar at the top of the right-hand area and click on the magnifying glass. A list of people matching the search criteria will be displayed. You can then continue the procedure from point 4 above.
If it is not there, you can create a person or convert an identity into a person as explained above.
Sometimes the system cannot automatically match identities because two people are so similar that it cannot tell them apart. In this case, you must look at the whole data set to determine the correct person.
Unmatching Identities and People
If a match was made but you realize that the identity is associated to the wrong person, you can dissociate them.
Note
If this error occurs after an automated match, review the matching rules.
To unmatch an identity from a person:
On the Menu Bar, click PEOPLE> Persons. The Persons page opens.
In the list, select the name of the person from whom you want to remove an identity (see Performing a Search in a Selection Page).
In the Persons Details page, under Identities click the identity you want to remove.

In the Associated Person list, erase the name of the person that you do not want to be linked to this identity and click Update.

The identity is no longer matched to the person and it appears once again in the list of orphan identities in the Identity Matching page (see The Identity Matching page).
Managing the employment situation for an identity
The employment status of an identity is managed via the following fields:
- Employment status
- End date of employment
Employment status has an internal value (specific to the RAC/M Identity solution) and a source value (imported from the identity source), which can be different from each other. If the identity is managed by RAC/M Identity and not imported from an HR source (as may be the case for some contractors), the two values will always be identical.
The internal value is always the one that will be used in the business logic and serves as an override of the state in the HR source. This makes it possible to deal with situations where a departure needs to be processed before HR can enter the necessary information. The source value represents the actual value in the identity source.
The columns in the IDENTIFICATION table that manage the status are SOURCE_EMPLOYMENT_STATUS_ID and EMPLOYMENT_STATUS_ID. The employment end date is in TERMINATION_DATE.
Important information on employment status
Employment status can contain a large number of values from different identity sources. You need to use mappings to map all these states to one of the actual states (Active, Inactive or Completed) that the solution uses in its business logic.
Relationship between different job fields
There is a precise relationship between the fields related to the employment situation, and this relationship dictates how the business rules are applied.
Employment end data (TERMINATION_DATE):This field is used by the solution to trigger an identity termination. The
ModuleHRTerminationDatemodule checks this date during execution and triggers termination by modifying the employment status. (EMPLOYMENT_STATUS_ID).Source employment status (HR_EMPLOYMENT_STATUS_ID): When this field changes following import from the HR source, it is automatically copied to the Employment Status field. (EMPLOYMENT_STATUS_ID).
This field also initiates employment status change processes when the effective employment status changes. For example, if an employee changes status from "Sick leave" (Inactive) to "Long-term leave" (Inactive), there is no change in effective employment status (Inactive -> Inactive) and therefore no process initiated. But if the employee goes from "Active" (Active) to "Retired" (Retired), the termination process will be launched.
Employment status (EMPLOYMENT_STATUS_ID): This field can change in several ways:
- Request of immediate termination in self-service
- When the end of employment date has arrived
- When source employment status changes
It is often used to temporarily replace (Override) the source employment status. Then, when the HR source changes to reflect the new status, the source employment status is copied to the employment status and the temporary replacement ends: both fields have the same value.
Employment status
The employment status of an identity can be modified directly in the administration page by changing its employment status or end date.
On the Identity details page, under Identities, consult the Employment status and Termination date fields.
It can also be modified by requesting a Employment Termination employee or a Employment Termination external contractor in self-service.
End of employment date allows you to change the status of an identity to Terminated by specifying the date on which it will no longer be employed. This is ideal for planning the departure of an identity and ensuring that its status is modified on the date of its end of employment.
Modification via import
Importing from the HR source to RAC/M Identity should only modify the HR fields, i.e. the source employment status (SOURCE_EMPLOYMENT_STATUS_ID). Similarly, RAC/M Identity will not modify the source field.
Connector and collector
See section Configuring an ICF connector and Creating a collector for data import
When a change in the source state is detected on import, RAC/M Identity compares the effective source state with the effective RAC/M Identity state. If they are not identical, this means a change in the state of the identity. A request for identity modification is therefore launched. In addition, the RAC/M Identity state is replaced by the source state just imported, and the event is audited.
Modification via a self-service request
It is possible to make requests in self-service, which may have the effect of modifying the status of an ident For example, it is possible to request the end of the use of an identity. When these requests are approved and completed, the RAC/M Identity status is modified according to the request. In the case of an end-of-employment request, the end-of-employment date will be changed to the chosen date.
Modification via administrator interface
It is only possible to modify the RAC/M Identity status via the administrator interface. The source state cannot be modified.
Impact of deactivation
Identity deactivation is usually temporary. Examples include sick leave and seasonal workers.
When deactivating an identity, RAC/M Identity will attempt to deactivate all the accounts it owns. These accounts will retain all the groups associated with them. This will make it easier to reactivate them should the need arise. To do this, RAC/M Identity will launch deactivation requests for these accounts.
Impact of activation
In the case of identity activation, RAC/M Identity will launch activation requests for accounts that have been previously deactivated by the solution.
Accounts not reactivated
If accounts were already inactive before the identity deactivation process was started, they will not be reactivated. This is necessary to ensure that the identity has no more rights when it is reactivated than it had when it was deactivated.
One consequence of this is that if the identity has not been deactivated via the RAC/M Identity solution, no account will be reactivated, as the solution does not know which accounts were active or not at the time of deactivation.
Take, for example, an active identity with two accounts: techadmin, which is active, and labadmin, which is inactive. The identity is deactivated. Consequently, its techadmin account is also deactivated. When reactivating the identity, only the techadmin account is reactivated. To activate labadmin, you would have to request it explicitly.
Impact of job termination
The end of an identity's employment is usually definitive. This may be due to retirement or resignation, for example. If a person whose identity has been terminated returns to the company, a new identity is usually created.
Consequently, an end of employment initiates a process of account termination. This process varies widely, depending on company practices and the assets involved. It can range from simple account deactivation to complete deletion.
Termination process does not imply completed status
The actions taken on an account during the termination process depend on the integration made for this asset. In particular, it is possible that the termination process simply deactivates an account. In this case, the effective status of the account will be "Inactive" following termination.
This may seem counter-intuitive, but it actually reflects the flexibility the solution offers. The solution allows you to define two different processes for accounts (deactivation and termination), but if this distinction is not necessary for a given asset, the two processes can be identical and the account will have the same state at the end of both processes.
Processing concurrent requests
- When an identity modification request is processed, all other modification requests made previously for this identity are cancelled.
Diagram
About Accounts
This section presents how to manage accounts in RAC/M Identitys.
Accounts allow people, automation and devices to access systems and applications. They usually consist of a user ID and password and are associated with access rights to perform certain functions or access certain information. Accounts are assigned to identities; therefore, a person may have different accounts under different identities.
Example
A developer has access to his Windows workstation, the issue tracking solution, and a code repository solution. He has accounts in each of those solutions and these accounts have to be associated to this identity. This same developer is also in charge of the Christmas party and uses other accounts for this particular project. When the Christmas project is over, these other accounts are no longer needed and may be deactivated.
Accounts are added to the RAC/M Identity and access repository by importing the data from data sources (see Importing persons and identities).
Personal and impersonal accounts
Personal accounts are those that belong to identities associated with people. Impersonal accounts are not associated with an identity or a person. For example, technical, system, generic and other accounts are impersonal accounts.
Trustees
In order to ensure sound governance of impersonal accounts, which are often high privilege accounts, they must be assigned to trustees. Trustees* are identities responsible for periodically reviewing the impersonal accounts assigned to them to validate their appropriateness.
If a trustee leaves the company or changes functions, the impersonal accounts assigned to the trustee must be reassigned to another trustee
Impersonal accounts must be revoked as soon as they are no longer required.
Matched and Unmatched Accounts
During import, the business logic attempts to match accounts to identities using a set of algorithms to identify matching identities to accounts with as much certainty as possible. If a match can be made unequivocally, the account goes to the matched state. However, in some cases it is not possible to match an account to an identity with certainty, so the account is placed in the unmatched state.
The business logic can be iteratively refined to improve the level of automated matching until only a small number of accounts remain to be manually matched. It is these accounts, which have not been automatically matched, that appear in this list and must be manually matched.
Note
Since impersonal accounts cannot be matched to identities, they will appear in the list of unmatched accounts until they are assigned to trustees.
The account matching page
The account matching page allows you to:
- Match personal accounts to identities
- Label accounts to organize them into categories
- Assign technical accounts to trustees

To facilitate navigation, search filters are available. On the left side of the screen are the account search filters, while the identity search filters are located on the right side of the screen.
Account Search Filters
The Label/Status field is used to determine which subset of accounts are displayed in the list. By default, unmatched accounts are displayed. If accounts have already been labeled, they can be displayed by selecting the appropriate label.
The Asset Grouping and Asset fields allow you to select a subset of accounts associated with the selected assets.
The list of accounts displayed can be narrowed down by selecting Show Only Active Accounts or by typing in a few letters of the accounts being searched. Finally, the Advanced Search button allows you to refine the search criteria.
Identity Search Filters
The list of identities proposed in the list on the right is based on the filters selected in the Suggestions section. These filters are used to suggest subsets of the displayed identities to facilitate matching.
| Filters | Description |
|---|---|
| Account Trustees | Proposes identities that are already account trustees. |
| Nicknames | Suggests identities whose nicknames (e.g., "Mike" instead of "Michael") may match the accounts to be matched. |
| Soundex | Suggests identities based on homophones of the last name. |
| Last/First Name Permutation | Suggests identities that can be matched by permutating the last name and first name. |
| Surname | Suggests identities based on the surname only. |
| Multiple Soundex | Proposes identities based on the homophones of the first and last name. |
Note
Based on the filters selected, RAC/M Identity will attempt to identify the most plausible identity for the match. If such an identity can be determined with a sufficient level of certainty, it will be pre-selected.
Tagging accounts
To facilitate the work of matching accounts, unmatched accounts can be grouped and tagged. Once tagged, they can be displayed in blocks and the business logic can be set up to perform specific processing based on the tags. The account matching page provides a number of standard tags at the bottom of the left window. In addition, you can define and assign your own tags.
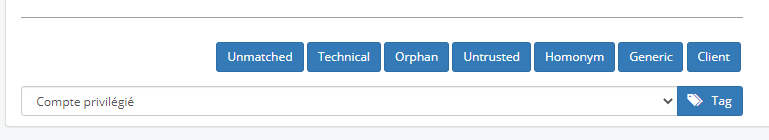
Note
The Unmatched button affects the status of the account. Accounts can be in either the Matched or Unmatched state and tagged with the labels below.
| Tag | Description |
|---|---|
| Unmatched | Places accounts in the unmatched state. This can be used to return one or more accounts that have been marked matched to the original state. |
| Technical | Designates technical accounts. These accounts will be assigned as trustee accounts to identities. |
| Orphan | Denotes accounts that cannot be associated with an identity. These accounts may represent some risk and should be revoked. |
| Untrusted | Accounts that cannot be quickly matched to an identity and require further investigation. |
| Homonym | These are accounts that cannot be quickly matched to an identity because there is more than one identity that may match the account. These accounts require further investigation. |
| Generic | Generic accounts are accounts that are used by multiple people. They cannot be matched to a single person. These accounts must be assigned to trustees. |
| Client | Refers to accounts that are owned by an entity other than the organization that is setting up the IGA service. This label is used in the context of outsourced services, where users of client organizations also have accounts in the IT systems. These accounts must be assigned to trustees. |
The drop-down list displays tags customized to your organization. It allows you to tag selected accounts with tags that are specific and relevant to your organization.
Example
Custom tags can be used to mark high-privilege accounts, for example, to help define high-privilege access review campaigns.
You can create custom tags in the CONFIGURATION>Mapping menu.
See also
To tag accounts:
On the menu bar, click PEOPLE> Account Matching.
By default, unmatched accounts are displayed in the list on the left.
Use the filters and the account search bar to refine the list of accounts to be tagged
Select the accounts you want to tag.
Click on one of the buttons at the bottom of the left hand section to tag the selected accounts or choose a tag from the drop down list at the bottom of the page and click Tag.
Matching Accounts to an Identity
If the system was not able to automatically match some accounts and identities because there are no unique identification keys, you will have to manually match them.
To match an account to an identity:
On the Menu Bar, click PEOPLE> Account Matching.
By default, the unmatched accounts are displayed in the list on the left. Use the filters and the account search bar to refine the list of accounts to match.
Select the account you want to match with a person.
Use the identity filters in the right-hand section to display potential identities.
Select the person and click the Match button.

The account and the identity have been matched. The account now appears in the list at the bottom of the Identity Details page.
Note
If several accounts with the same nomenclature are detected, a panel will be displayed that will offer you to match all similar accounts in bulk. This makes the manual matching work much easier and faster.
Unmatching Accounts from an Identity
Inversely, if a match has been made and you find that it should not have, you can remove an account from an identity.
To unmatch an account from an identity:
- Click PEOPLE> Identities.
- In the Search text box, type a few letters of the name or first name of the identity for whom the account has been linked to and click the magnifying glass.
- In the list, click on the identity. The Identities Details page opens.
- Under Accounts, click the
button next to the account you want to remove.

- Click OK to confirm.
The account is no longer matched to the identity and is moved to the list of orphan accounts in the Account Matching page.
Assigning accounts to trustees
In the menu bar, click PEOPLE> Account Matching.
By default, unmatched accounts are displayed in the list on the left.
Select the unmatched Technical or Generic accounts.
Use the filters and search bar to refine the list of accounts to be assigned.
Select the accounts you wish to assign. Use the identity filters in the right section to display potential identities.
Select an identity from the list and click the Match button.
See also
Transferring an Account
When you already know who the account belongs to, you can transfer it directly from one identity to another instead of removing it and then matching it again.
To transfer an account:
- On the Menu Bar, click PEOPLE> Identities.
- In the list, click the person whose account you want to transfer to another identity. The Identities Details page opens.
- Under Accounts, click the
button next to the account you want to transfer.

In the Account Transfer dialog box, in the Identity selection list, type the name of the identity to whom you want to assign the account or select it in the list.
Click Transfer.
The account now appears in the list of accounts in the identities's "details" page.
About Assets
This section presents the procedure to create and manage assets in RAC/M Identity.
In RAC/M Identity, an Asset is any component owned by the organization that people use to conduct business and that requires access privileges, whether logical or physical. Assets can be, for example, systems, applications, infrastructure components, or even physical items.
In this context, the payroll system, business software, messaging system, wireless network, cloud applications, doors, etc. are all examples of assets.
To create and manage assets, you will use the ASSETS option in the main menu.
The ASSETS option on the main menu allows you to:
- View, modify and add Asset Groupings
- View, modify and add Assets.
- View, modify, add and remove Access Accounts.
- View, modify, add and remove Groups.
- View, modify, add and remove Items.
- View, modify, add and remove Permissions.
- View, modify, add and remove Delegation Groups.
Asset Grouping
In order to facilitate management, assets are always associated with an Asset Grouping. By default, assets are associated with the Default grouping. You can create as many asset groupings as you wish and assign all the required assets to them.
Example
If your company has several independent entities that use similar IT systems such as Active Directory or Office 365, it may be useful to create asset groupings by entity. This way, there will be no collision on asset names, even if the assets are the same in the different entities because the assets are referred to by the canonical form "Asset Grouping/Asset".
Account Selection Strategies
When access to an asset is granted to an identity, an account must be created and when accesses are to be removed, accounts must be revoked. RAC/M Identity incorporates several strategies for creating or selecting accounts in an automated provisioning and de-provisioning environment.
The drop-down lists provide several policies along with a short description. Strategies selected at the access grouping level apply to all assets associated with the grouping if specific strategies have not been assigned to the assets. In general, strategies that return multiple or all accounts are more appropriate for deprovisioning, while provisioning policies need only select or create a single account.
The strategies differ on how the account(s) are selected. Here is a brief description of the available strategies.
Select Any Active Account selects an active account that can be found on any asset the target identity has access to. If no account is found, an account will be created using the account creation policy associated with the asset.
Select All Accounts selects all accounts, active and inactive, belonging to the target identity on the assets associated with the grouping. This strategy is typically used to remove all accounts from an identity during deprovisioning.
Select all active accounts selects all active accounts belonging to the target identity on the assets associated with the pool. This strategy is typically used to remove all accounts from an identity during deprovisioning.
Selecting an active account or creating/activating one based on the identity's primary account will select an active account if there is only one, otherwise an error will be returned. If there is none, a new account will be created or reactivated using the contents of the Primary Identity field of the targeted Identity object. If this field is empty, a new account will be created using the account creation policy associated with the asset. This strategy is recommended for provisioning.
Selecting an active account or creating/activating one based on the identity email will select an active account if there is only one, otherwise an error will be returned. If there is none, a new account will be created or reactivated using the contents of the Email field of the targeted Identity object. If this field is empty, a new account will be created using the account creation policy associated with the asset. This strategy is recommended for provisioning.
Note
The content of the drop-down lists may change as RAC/M Identity evolves. Refer to the drop-down list contents and associated description to select the appropriate policies.
Creating an asset grouping
To create an asset grouping:
On the Menu Bar, click ASSETS> Assets Groupings.
At the top right of the page, click the
button.
Enter the required information as follows:
Name
Write the name of the asset grouping. Choose a name that is meaningful and representative of the grouping.
Description
Enter a brief description of the grouping. It will help pilots distinguish between the different asset groupings.
Status
In the list, select Enabled to enable the assets associated with this grouping. This means that they will be visible to the business logic, which can process the access data associated with these assets and take action if necessary.
Select Disabled to disable all assets associated with this grouping. In this case, the assets will not be visible to the business logic and no analysis or action will be taken.
Tip
The Disabled state can be useful when the assets associated with the grouping are in the process of being integrated or if the grouping represents separate environments that do not need to be activated momentarily.
Technical Name
Enter a name that will be used by RAC/M Identity as a unique key. A good technical name should be unique, permanent and reflect the associated object. example: Medusa_prod_Mtl.
Provisionning
Under Provisioning, from the drop-down lists, select the most appropriate account selection strategies for provisioning and deprovisioning. See Account Selection Strategies.
If you leave these fields blank, the strategies associated with the assets will be applied.
- Under Notification
- This configuration controls whether an email is sent when an account or a group in this asset grouping is provisioned. The email is sent to the specified recipient(s).
- Select the level of granularity for Accounts and Profiles to configure for notifications related to provisioning events.
- Under Notification
If extended attributes have been added to the Asset Grouping object, you can enter the appropriate values there.
Click Save.
The asset grouping is added to RAC/M Identity. This grouping is now available to associate with assets.
Modifying an asset grouping
To modify an asset grouping:
On the menu bar, click ASSETS> Asset Groupings.
Select the asset grouping you want to edit. You can navigate directly to the lists of Assets, Accounts, Groups, Items and Permissions associated with the selected grouping by clicking on the respective buttons.
Make the necessary changes.
Click Save.
Remove an Asset Grouping
It is not possible to remove an asset grouping.
Creating an asset
In most cases, assets must be created manually, directly in the management console. However, there are a few situations where assets can be added to the RAC/M Identity repository by importing data from data sources (see Data Analysis).
This is the case, for example, for servers or applications that use a common flat file format to extract accounts and associated access. This is also the case for servers or equipment whose configuration is documented in a configuration management database CMDB. In both cases, assets can be created automatically in the repository without human intervention.
When creating an asset you can enter the metadata and configuration items that determine the level of integration as well as the details of how the business logic works with respect to that asset. Of course, the level of integration may evolve over time as your organization matures with respect to IAM processes. The configuration details of the targeted assets will need to be adjusted accordingly.
To manually create an asset:
On the Menu Bar, click ASSETS> Assets.
At the top right of the page, click the
button.
Enter the required information as follows:
Name
Type the name of the asset. Choose a name that is meaningful and representative of the asset.
Technical name
Enter a name that will be used by RAC/M Identity as a unique key. A good technical name should be unique, permanent and reflect the associated object. example: Medusa_AD_MTL.
Status
In the list, select Activated to activate the asset. This means that it will be visible to the business logic, which will be able to process the access data associated with this asset and take action if necessary.
Select Disabled to disable the asset. In this case, the asset will not be visible to the business logic and no analysis will be performed or action taken.
Description
Enter a brief description of the asset. It will help operators distinguish between different assets.
Asset Grouping
Select or type in a few letters to find the asset grouping you want to associate the asset with. (See also Creating an Asset Grouping)
Password synchronization source
If you plan to implement password synchronization, you can select the Asset to be the source. That is, when a password change is made on the source asset it will be propagated to all assets that use it as a source. Typically, the recommended sources are Active Directory or Entra ID.
To register a source asset, select or type in a few letters of the asset you are looking for.
Leave the field blank if you do not plan to implement password synchronization.
Category
Categories allow assets to be logically grouped for specific analysis and processing. Categories can be defined arbitrarily which provides a lot of flexibility to represent a structure relevant to your organization.
For example, categories can be defined to group assets by criticality level. Another possibility is to group assets by type of system such as financial systems, HR systems, business systems, etc.
Select a category from the drop-down list to categorize the asset if desired. You can leave the field blank if categorization is not required.
Note
Categories must have been previously created in the CONFIGURATION Mappings section to be available in the drop-down list.
DN
DN stands for Distinguished Name. This field is used mainly with LDAP and X500 directories. You can leave this field blank for common assets.
System Type, OS and Identifiers
These fields are optional informational fields that can be used to provide additional information to the business logic. You can use them to identify the nature of the system or a server as well as the operating system if relevant. The identifiers fields can be used for any additional information that may be useful to the business logic.
Leave the fields blank if not required.
Date of last validation, date of last modification and date of last validation.
These fields are indicators, updated by RAC/M Identity to reflect the dates of events impacting the asset.
Access Service Provider
This checkbox is used to indicate that the asset is used to control access to other assets. LDAP directories and databases can be used as Access service providers. For example, Active Directory or Entra ID groups are often used to control access to assets that outsource authentication and authorization, such as Citrix, BitWarden, etc.
This allows the business logic to handle the asset's security groups in a way that controls access for the assets that depend on them.
This box is typically checked for an Active Directory or Entra ID directory used to control access to assets configured as Logical Applications. Leave the box blank for all other cases.
See also
Entitlements Available through Self-Service
When you select this check box, you allow access requests to this asset to be made in the self-service portal.
Voir aussi
Click Save at the bottom of the page to save the asset. The asset is added to RAC/M.
Note
It is recommended to save the asset being created even if the configuration is not completely finished.
Accounts, Groups, Items, Permissions buttons
These buttons point directly to list pages that display the items represented by the buttons. As the asset is being created, these lists are empty and of no interest at the moment. You can go directly to the Provisioning section.
Provisioning
Provisioning, from the drop-down lists, select the most appropriate account selection strategies for provisioning and deprovisioning. See Account Selection Strategies.
If you leave these fields blank, the strategies associated with the asset pool will be applied.
- Under Notification
- This configuration controls whether an email is sent when an account or a group in this asset grouping is provisioned. The email is sent to the specified recipient(s).
- Select the level of granularity for Accounts and Profiles to configure for notifications related to provisioning events.
Owner
In the list, type the first few letters of the name of the owner and select it.
An owner must be designated for each asset. The owner is responsible for the sound management of the asset and may be involved in approving access requests and/or reviewing and certifying access, especially for high privilege access.
Select the asset owner by entering a few letters of the owner's name in the drop-down list.
Administrator Group
This field allows you to assign a delegation group that corresponds to the team responsible for managing the asset, especially for executing access requests and revocations. Members of this group will be the ones to receive access requests once they are approved, as well as access revocation requests in cases where provisioning and de-provisioning are not automated.
Select the asset's administrator group by entering some letters of the group in the drop-down list.
Tip
It is recommended to register an administrator group when implementing a new asset to ensure the creation, modification and removal of access until provisioning and de-provisioning can be fully automated.
Note
Administrator groups must be created beforehand. See Creating a delegation group
Reviewer Group
This field enables you to assign a delegation group that corresponds to the team responsible for reviewing the asset. Members of this group will be responsible for approving or rejecting elements within review campaigns.
To select the asset's reviewer group, simply enter a few letters of the group in the drop-down list.
Extended attributes
If extended attributes have been added to the Active object, you can enter the appropriate values.
Define approval flow
RAC/M Identity includes an advanced and highly flexible approval flow feature that allows you to define a mode of operation with up to three levels of approval by simple configuration.
The activation of each level is optional, and can be determined based on the level of risk associated with the asset itself and the underlying groups. Each level corresponds to a step that must be completed in order to proceed to the next. Each level can invoke delegation groups to ensure that approvals are completed as quickly as possible, even in the event that stakeholders with approval responsibilities are unavailable.
For each of the following levels, indicate whether the level is required and complete the information indicating who will be required to approve the requests, if applicable.
Identity-Based Approval
Select Required if the person responsible for the person requesting access must approve access to this resource. In this case, the Approver Group defined at the identity level will be used.
Group approval
Select Required if the resource owner (active or group) or a delegation group must approve access to this resource.
If a delegation group must approve the request, select it from the drop-down list.
Note
Delegation groups must be created beforehand. See Create a delegation group
Special approval
Select Required by this special approval group if you need a third level of approval.
This can be useful, for example, to grant access to a critical resource for which specific training or certification is required.
If a delegation group must approve the request, select it from the drop-down list.
Note
Delegation groups must be created beforehand. See Create a delegation group
- Under Notification
Click Save to save the asset.
Viewing or modifying an asset
To view or edit an asset:
- On the ASSETS menu, click Assets.
- In the list, under the Assets column, select the asset you want to view or edit. Make the required changes
- Click Save to save your changes.
Adding an existing asset to an asset grouping
To add an existing asset to an asset pool: 1.
On the ASSETS menu, click Assets.
In the Asset Grouping list, select the asset you want to add to the grouping.
Assets for which an asset grouping has not been specified will be in the Default grouping.

On the Asset Details page, from the Asset Grouping drop-down list, select the grouping you want to add the asset to.

Click Save.
The asset is now associated with the asset grouping. You can view all asset details and associated access and permissions on the Asset Grouping Details page.

Creating a Delegation Group
A delegation group is a group of identities to which the group owner has delegated responsibilities. For example, members can approve an access request if the group owner is not available to do so.
To create a delegation group:
On the Menu Bar, click ASSETS> Delegation Groups.
At the top right of the page, click the
button.

Under Details, enter the required information as follows:
Name
Type the name of the group. Choose a name that is meaningful and representative of the nature of the delegation group.
Tip
It is a good practice to use a standardized syntax for delegation groups that includes the use and the name of the owner. ex: GD-APP-Charles Tremblay.
Description
Type the description of the group responsibilities.
Group Type
From the drop-down list, select a delegation group type. RAC/M Identity includes two basic types of delegation groups, SIMPLE_GROUP and CASCADE_GROUP.
SIMPLE_GROUP groups direct requests to all members simultaneously. In this mode, all members receive notifications and see the tasks in the self-service portal. As soon as one member approves a request, it is removed from the list. This approach ensures the fastest resolution of requests.
CASCADE_GROUP groups direct requests sequentially to each member according to the priority specified in the Priority field associated with each member and the configuration settings. This approach is useful for defining a gradual strategy for approving requests.
The two types of groups exist in two versions, the basic versions that include the group owner, and the SIMPLE_EXCL_OWNER and CASCADE_GROUP_EXCL_OWNER versions that exclude the group owner, i.e. requests are forwarded to all members except the group owner.
These versions are useful for delegation groups whose owners are executives with little or no availability for operational tasks.
Group scope
Delegation groups with a scope of Generic can be used for all approval or certification tasks. They will be available in the drop-down lists of the various objects that require delegation groups.
Delegation Groups with a scope of Self Service are used to specify that individual members can see the accesses held by an individual in the self service portal.
Delegation Groups of type Self Service must be associated with members of Approver Groups assigned to identities in order for them to see the accesses currently held by those identities.

Note
If the requester is not a member of the Approver Group nor a member of a Self-Service delegation group belonging to one of the members of the Approver Group of the person whose rights he wants to view, he will be able to make the access request but will not be able to view the existing accesses or remove them.
Technical name
Enter a name that will be used by RAC/M Identity as a unique key. A good technical name should be unique, permanent and reflect the associated object. example: GD_APP_CT.
Owner
In the list, select the arrow to open it or type the first few letters of the owner identity name, then select it.
Delegates
Under Delegates, in the Search for Delegates list, type the first few letters of the name of the identity you want to add to the members and click the Add button.
Priority
The Priority field allows you to implement a progressive escalation strategy by staggering notifications to individual group members after a number of reminders determined by the value of the Priority field.
Example
A value of "1" means that the member will be notified after each callback, while a value of "3" means that the member will be notified after three callbacks.
Click on Save.
Viewing, modifying or removing a delegation group
To view, modify or remove a delegation group:
- On the ASSETS menu, click Delegation Groups.
- In the list, select the delegation group you want to view, edit or remove. Make the required changes or click on the
button to remove it.
- Click Save to save your changes.
About Managing Access Rights
This section describes how to manage access rights in RAC/M Identity.
In RAC/M Identity, Access is a generic term that represents an access right, privilege, or permission that allows a user to access an asset or function of an information asset, or to access a physical asset such as a key or access to a door.
To create and manage accesses, you use the ACCESS option in the main menu.
The ACCESS option in the main menu allows you to:
- View, modify, create and delete Access Review Campaigns.
- View, modify and create Roles.
- View, modify and create Role Versions.
- View, modify and create Role Modeling Sessions.
- View, modify, add and remove Task Segregation Rules.
- View, modify, add and remove Business Functions.
About Access Review Campaigns
During an access review, designated reviewers review all accesses and determine if they are still valid or if they should be removed. This way the accesses are certified as valid.
RAC/M Identity offers a great deal of flexibility in defining access review campaigns to allow for a sustainable and efficient process that is well suited to each organization's needs.
Campaigns can be configured to determine the content and level of detail to be reviewed, the reviewers involved and the scope in terms of identities and assets included.
The exact behavior of the campaigns as well as the capabilities of the reviewers are also fully configurable.
In addition, incremental campaigns reduce review efforts by focusing on changes made since the last review.
Note
Access review is also often called recertification, access validation or access verification.
Note
To perform access review after the campaign has been launched, see Access Review Tasks.
Creating or Modifying Filter Rules (Filters)
This section describes how to define filter rules using the Rule Editor. The rule editor is used in several places in RAC/M Identity.
The purpose of filter rules is to produce a subset of objects on which processing will be performed by the business logic. The objects selected are determined based on the conditions you define and the content of the attributes evaluated by the conditions.
Filters are built by combining simple rules, each evaluating a single condition using the Boolean operators AND and OR. Rules can be grouped and subgroups combined in the same way. All rules and subgroups within a group or subgroup use the operator associated with the group.
Filtering rules are used in two main cases:
- To filter identities, or
- To filter assets.
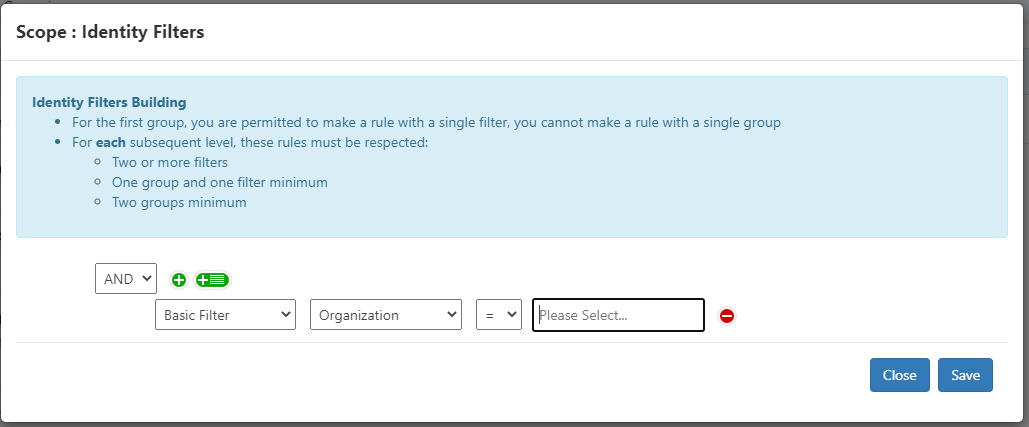
Rules
The rules are built with a simple syntax:
[Boolean Operator]
[Attribute Source] [Attribute] [Equality Operator] [Value] Rule 1
Rule 2...
- Boolean Operator applies the selected function to all rules and subgroups within a group.
- Attribute Source contains a drop-down list that refers to an attribute source:
Basic Filter offers the attributes of objects:
- People and Identity (identity filters) or
- Asset grouping*, Assets, Accounts, Groups, Items (asset filters)
- Other attributes*, (asset filters).
Extended attributes xxx The list also proposes the extended attributes associated with the objects in the list. Only objects relevant to the filters to be built are displayed in the list.
- Attribute Select the attribute you want to evaluate in the rule.
- Equality Operator select = or != depending on whether the attribute should have a value equal or different to the value determined.
- Value enter the desired value.
Note
The = operator also acts like the contains operator if the attribute contains a list of values.
Example
If the extended identity attribute Certifications contains the values: "HIPAA", "FDA", "NERC", the rule:
Expanded identity attributes Certifications = FDA is true.
To create a filter rule:
Navigate to the page of the object you want to add a filter rule to, such as Access Review Campaigns and Roles. Click on the buttons to add or edit the rules.
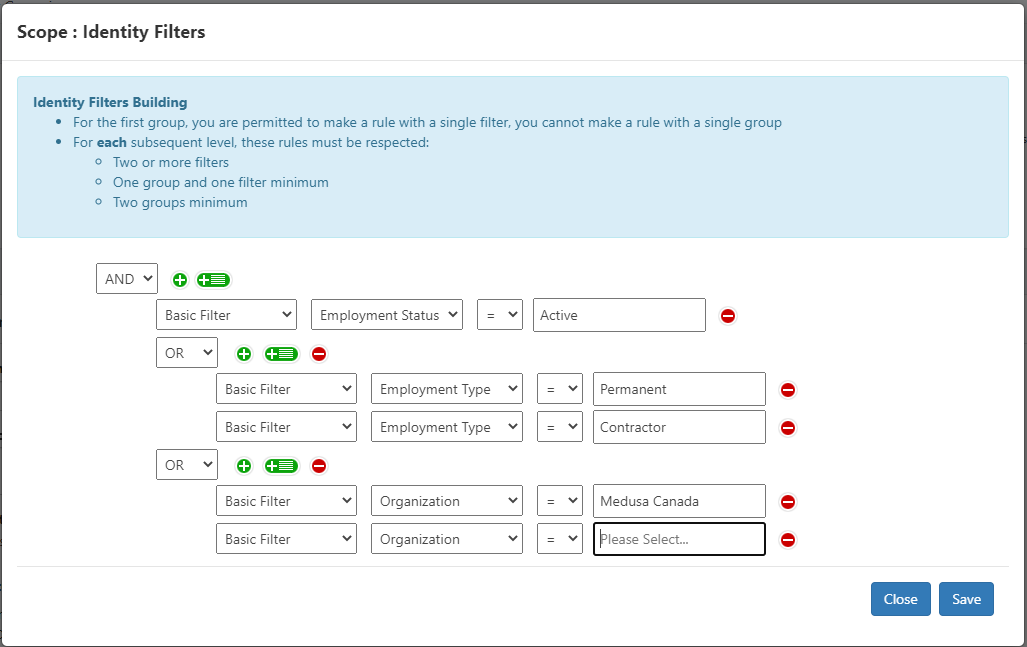
Select the equality operator you want to use for the associated group:
- AND : The result is true when all rules and subgroups are true.
- OR : The result is true when any of the rules or subgroups are true.
Click the
button to add rules to a group.
Click the
 button to add a subgroup of rules.
button to add a subgroup of rules.Click Save. The filter rules are saved to the repository.
Creating an access review campaign
To create an access review campaign:
On the Menu Bar, click ACCESS> Review Campaigns.
At the top right of the page, click the
button.
Under Campaign, enter the required information as follows:
Name
Type the name of the campaign.

Description
Type the description and goal of the campaign.
Click Save.
Start Date and End Date
The Start Date displays the date the campaign will be started. The End Date opens a calender in which you select when the campaign will end.
Mode
Select Interactive Campaign to process the campaign online. The Offline Campaign option produces PDF reports that reviewers review. This option is obsolete and will be removed in a future version.
Under Campaign Type and Scope, you can define the nature of the accesses to be reviewed, the level of detail and the scope. Enter the required information as follows:
Campaign Type
Access review campaigns are organized into three themes:
- Identity reviews
- Role content reviews
- Trustee Account Reviews
For Identity Reviews
- All entitlements: Allows you to review all accesses and permissions granted to identities.
- Excess Roles and Entitlements: Allows you to review the roles granted to identities as well as all accesses and permissions granted in addition to those granted by the roles.
- Only excess role entitlements: Allows you to highlight and review accesses and permissions granted to identities in addition to those granted by roles.
- Only segregation of duties conflicts: Allows you to review access and permissions granted to identities that violate segregation of duties rules.
- Only show accounts (entitlements assigned to accounts are excluded): Allows for a simplified review of access accounts held by identities without further detail on groups and permissions.
For Role Content Reviews
- Included roles and entitlements: Allows you to review all access and permissions associated with roles.
For the Trustee Account Reviews
- All entitlements: Allows you to review all access and permissions associated with impersonal accounts.
- Show Accounts Only (rights for these accounts are not displayed): Allows you to perform a simplified review of impersonal accounts without further detail on groups and permissions. This allows trustees to quickly confirm the validity of impersonal accounts.
Trustee accounts
Check this box if you want to include impersonal accounts in an identity review campaign.
Note
This option is only available when Identity Review - All entitlements or Identity Review - Show Accounts Only... is selected.
Additional Filter
Check this box to include inactive identities in an identity review campaign.
Note
This option is only available when Identity Review - All entitlements is selected.
Reviewers
To determine who will review and certify accesses, select one of the following options:
Identity reviewers when you want the reviewers to be those assigned to the identities.
Example
The reviewer can be the line manager or any other relevant identity depending on the hierarchical level and organizational structure.
Asset Reviewers when accesses are to be reviewed by asset reviewer.
This type of campaign is particularly useful for conducting high privilege access review campaigns.
Designated reviewer when you want to specify a specific reviewer for the entire campaign.
A reviewer can be explicitly assigned to each identity by business logic that can apply custom business rules to determine who to assign.
This type of campaign is particularly useful for conducting highly targeted, limited scope access review campaigns.
Reviewers of the entitlements given by the roles (assets, groups or included roles)
Available only for campaigns type Role Content Review - Included roles and entitlements
When this option is selected, the reviewer will be determined according to the elements contained in the role, which will have to be reviewed to determine whether their entitlement should be included in this role. These entitlements will be assigned to an identity when the role is assigned to it.
Identity and Asset Filters
To create an identity filter
Click the Edit button to add rules to filter the identities you want to include in the campaign. For example, you can perform access reviews by department, organization, or any other logical way to determine which identities to review.
Leave the field blank to include all identities.
Click the Delete button to delete the rules.
See also
To create an asset filter
Click the Edit button to add rules to filter the assets you want to include in the campaign. For example, you can perform access reviews for all systems or for a subset of assets.
Leave the field blank to include all assets.
Click the Delete button to delete the rules.
Role campaign scope
Select one of the following options to specify the scope of role reviews.
- Active Roles The campaign will focus on active roles only.
- Latest role versions The campaign will include the latest versions of all roles, whether they are active or not.
- Roles included in role modeling sessions The campaign will include all roles, organized by role modeling session.
- Role versions The campaign will include all roles organized by version.
Advanced Configuration
This section allows you to configure several settings that define how campaigns work as well as the options available to reviewers.
Items without approvers
This option allows you to determine how items for which approvers could not be resolved are handled.
Under Advanced Setup, select one of the following options:
- Excluded from Campaign if you want to exclude items for which an approver could not be determined.
- To Review by Campaign Manager if you want items for which a reviewer could not be determined to be reviewed by the Campaign Manager.
Note
These options are not available if the reviewer choice is Designated reviewer.
Approval
These options determine the choices available to reviewers when approving items during access review. Check the appropriate options.
End of Campaign
Check this box if you want reviewers to authenticate when completing their campaign. This option increases the assurance level of the certification process by using explicit authentication as proof of presence.
Allow reassignment of items to be reviewed
These checkboxes determine whether, and to whom, reviewers can transfer review items that they cannot review for any reason. Check the appropriate boxes.
- To the Campaign Manager allows certificants to transfer review items to the Campaign Manager.
- To other reviewers in the campaign allows reviewers to transfer items to other reviewers in the campaign.
- To any identity allows reviewers to transfer items to any identity.
Incremental Campaign
This section allows you to determine which campaigns to use as the baseline for incremental campaigns.
Incremental campaigns are based on campaigns that are similar in three criteria:
- The Campaign Type
- The Approvers
- The campaigns must be Completed.
The campaigns that match these three criteria appear in the list at the bottom of the section.
Use the parameters and the search field to display the desired reference campaigns. In general, it is best to select the most recent campaigns.
Select which campaigns to use by checking the boxes to the left of the campaign names. The incremental campaign will highlight changes that have occurred since the set of campaigns that make up the baseline.
Note
A revision campaign becomes incremental by selecting reference campaigns.
Notifications
Under Notification, you can determine the email template to use as well as the callback and escalation settings.
Template
In the Template field, you can choose the email template to use for reminders. You can use the basic template provided with the solution or you can use a custom template based on your company colors, logos and messages.
Select the desired template from the drop-down list. A preview of the selected template is displayed in the right window.
See also
See the RAC/M Identity - Personalization Guide for more details on how to create or modify email templates.
Email Reminder Interval (days)
In the Email Reminder Interval (Days) field, enter the number of days between sending reminder emails to approvers who have not completed their access reviews.
Escalation
This field is used to determine if reminders will be escalated to the supervisor of approvers who are late in completing their access review. From the list, select:
- No if no escalation is desired;
- Last Notification if an email should also be sent to the supervisors of certificants who have not yet completed their review at the last scheduled reminder;
- Last two notifications if the escalation email should also be sent if the reviewers have not yet completed their access review at the time of the next to last scheduled callback.
Note
The configuration of the reminders (delay and type) is done in the configuration file config.properties (CONFIGURATION> Configuration file).
Click on:
- Save to save the campaign without changing its status.
- Save and Preview to save the campaign and view the campaign's reach and impact
- Save and Start to save and start the campaign.
Important
You cannot make changes to a campaign once it has been launched, except to extend the end date.
We strongly suggest that you use the Save and preview mode in order to view and validate the content that the reviewers will have to review. If everything is in order, you can start the campaign.
Starting and Tracking a Review Campaign
Starting an access review campaign only requires a few steps.
To start the review campaign:
- On the Menu Bar, click ACCESS> Review Campaigns.
- On the Campaigns Selection page, click the campaign you want to start.
- At the bottom of the Review Campaign Details page, click Start.
The campaign starts, its status is In Progress.
On the right of the Campaign section, click the button to open the description of what was used to create the campaign.
The top of the section displays the time left on the campaign, its status, and percentage of completion.
Statistics about the evolution of the campaign are shown as graphics. Next to the graphics, there is a list of the reports generated for this campaign. These reports are generated when you click the Reports button at the bottom of the page.
The last part of the panel presents one of two possibilities:
Online campaign: A list of reviewers showing their phone number, email, and progress. You can click a reviewers to access his campaign information Details page.
The Actions list allows you to do two things:
- Transfer reviewer’s tasks: Opens the dialog box which allows you to choses someone to transfer the tasks to.
- Send reminder email: Instantly sends a reminder email to the reviewer.

The Transfer Reviewer's Task dialog box
- Offline campaign: A list of Excel and PDF documents. Columns show the icon representing the document type, name, and creation date (day/month/year format).
Ending a Review Campaign Manually
By default, an access review campaign is automatically ended when the end date is reached. If you see, however, that all the accesses were reviewed before that date, you can close the campaign manually.
To stop a review campaign:
On the ACCESS menu, click Review Campaigns.
On the Campaigns Selection page, click the campaign you want to stop.
At the bottom of the Review Campaign Details page, click End Campaign.
The campaign status becomes Ended. Managers and resource owners can no longer accept or revoke accesses within that campaign.
For more information on tracking accesses and accounts, refer to Access Review Tasks.
Canceling a review campaign
You can cancel an Access Review Campaign.
To cancel a review campaign:
On the ACCES menu, click Review Campaigns.
On the Campaigns selection page, click the campaign you want to cancel.
At the bottom of the page click Cancel.
The status of the campaign changes to Cancelled. Managers and resource owners can no longer accept or revoke access within this campaign.
Viewing or Modifying a Review Campaign
To view or edit a Review Campaign:
- On the ACCES menu, click Review Campaigns.
- On the Campaigns selection page, click on the campaign you want to view or edit.
- Make the required changes
- Click Save to save your changes.
About Role Modeling
The goal of role modeling is to develop an optimal model, in which the majority of entitlements are granted by the minimum number of roles without increasing the security risk by giving too broad accesses.
Role modeling is essentially done in two complementary ways:
- By mining
- By manual refinement, often also called modeling.
Role mining takes advantage of the analytical functions of the repository to determine common accesses held by multiple individuals, represented by identities. Commonly held accesses become the basis for roles defined by mining.
Manual fine-tuning allows the exact content of roles to be determined to properly define the required access.
There are several schools of thought and just as many role modeling strategies that can be used depending on the human, organizational and technological context of each organization.
RAC/M Identity contains the necessary functions to model roles according to the RBAC model in accordance with the ANSI/INCITS 359-2012 standard. The solution also offers advanced features for automatic role assignment, meeting the objectives of the ABAC model.
See also
Creating a Role Modeling Session
In RAC/M Identity, the Role Modeling Sessions page allows you to experiment with the role model without impacting production until you are ready to deploy the new role.
Important
Only click the Activate button when the role is satisfactory. If you want to make other changes, you will have to start over with another version of that role or create a new one.
To create a role modeling session:
In the ACCESS menu, click on Role Modeling Sessions.
At the top right of the page, click the
button.

On the Role Modeling Sessions page, in the Session text box, type the name of the session.
In the Description text box, type a description of this session.
Click Save.
The new session is created.
The next step is to create roles associated with this session.
See also
Once the roles have been created and refined, you need to complete the assignment of the roles to the session.
Assigning Roles to a Modeling Session
The Roles section allows you to determine which roles are associated with a modeling session. The selected roles can then be activated or deactivated as a whole if desired.
Note
You must have created roles before you can assign them to a modeling session.
To assign roles to the modeling session:
If you are already on the Details page of a modeling session, go directly to step 4.
On the ACCES menu, click Role Modeling Sessions.
Select the desired session from the list.
The Details page for the role modeling session will open.
By default, the Available Roles list displays all available roles in the repository.
You can narrow the list by either displaying the roles associated with a selected modeling session in the Session Role Selection drop-down list or by applying an advanced filter as follows:
- Filter By Select the RAC/M Identity object or associated extended attributes to use as a filter.
- Additional Filter Select the attribute to use
- Value Enter the value of the attribute that matches your search criteria.
Click Apply Filters to perform the search.
Select the role(s) to be assigned in the area on the left.
Use the arrows in the left area to move the desired roles to the right area. You can remove selected roles from the right area by using the arrows on the right
Click on Save to save the session.
You can also remove a selected role by clicking the button.
Creating a new role by mining
To create a new role by mining
If you have just created a role modeling session, go directly to step 4.
Otherwise,
On the menu bar, click ACCES> Role Modeling Sessions.
Select the modeling session to which you want to add a role.
To the right of the Role Mining section, click the
button.
Click on the New Role button.

In the Role Name text box, enter the name of the role.
In the Entitlement Inclusion Threshold field, enter a percentage. This percentage determines the percentage of identities, from the selected population, that must have access in order to be included in the role.
Example
You want to create a role for cardiologists working at St-Gabriel hospital. Several cardiologists use the PCS application and you set the Inclusion threshold to 90.
When you generate the session, if 90% or more of the cardiologists working at this hospital share this access, then the PCS access will be included in the role. If less than 90% of the cardiologists at St-Gabriel have this access it will not be included in the role.
Tip
Choose a very low value (e.g. 1%) to include all (or the majority) of the accesses held by the selected identities.
Choose a high value (e.g. 99%) to include only the accesses held by all the identities.
A value of 60% to 80% is a good starting point.
Caution
Pay particular attention to the results obtained if the number of identities analyzed is very small. For example, if only 3 identities meet the filtering criteria and the inclusion threshold is set to 80, only the accesses held by all the identities will be included.
Check the Include Inactive Accounts box if you want the role drill to consider inactive accounts and associated access.
Scope
You need to define which identities and assets to mine the role.
Click the Identity hyperlink or the corresponding Edit button to edit the identity filter.
Click the Assets hyperlink or the corresponding Edit button to edit the asset filter.
Click on the Clear button to clear the filters.
For the complete procedure on how to set filters, see Creating or Modifying Filter Rules.
Click the Generate button to generate the role.
RAC/M Identity scans its repository and builds the role by mining all identities and assets that match the selected filters and settings.

Click the Click here to edit this role link located in the green band at the top of the screen to complete the role definition.
This action opens the Details page which allows you to complete, edit and revise the newly created role.
The role is created and added to the modeling session. You can continue to refine the role until it is satisfactory.
For more information on editing and revising roles, see Editing a Role.
Creating multiple roles by mining
This button allows you to generate multiple roles according to specific criteria. For example, you can automatically drill down to all the roles of a department, a division, an organization or even the entire company.
In general, the best results are obtained by limiting the mining of multiple roles to relatively small, homogeneous entities.
Example
You can drill down and automatically generate all the roles in a department. For example, in a hospital you could mine all roles in the cardiology department at once.
To generate several roles at once:
If you have just created a role modeling session, go directly to step 4.
On the ACCES menu, click Role Modeling Sessions.
Select the modeling session to which you want to add roles.
To the right of the Role Mining section, click the
button.
Click on the Multiple Roles button.

Enter the information in the fields as follows:
In the Role Name Prefix text box, enter a prefix that will be added to all role names that are created.
This is used to identify them on the Role Versions page.
Note
Do not add spaces or punctuation characters after the prefix. The "-" characters will be inserted automatically between the prefix and the role name derived from the value of the variable attributes.
In the Entitlement inclusion threshold field, enter a percentage. This percentage determines the percentage of identities, from the selected population, that must have a specific entitlement in order for it to be included in the role.
See Creating a new role by mining for more details on the Entitlement inclusion threshold.
Check the Include Inactive Accounts box if you want the role mining to consider inactive accounts and associated accesses.
Scope
In the Criteria: Filters dialog box, in the lists, select the filter type and validate or edit the rules.
Under Variable Attributes for Multiple Role Creation, next to Identity, click the Edit button.
Enter the name of the attribute whose values will be listed to create the set of roles.
Example
If in the cardiology department of St-Gabriel hospital, there are three different titles such as "Cardiologist", "Attendant" and "Generalist".
The identity filter could be:
Organization = St-Gabriel
Department = Cardiology
And the variable attribute: Title
This would generate the following roles:
- St-Gabriel - Cardiology - Cardiologist
- St-Gabriel - Cardiology - Attendant
- St-Gabriel - Cardiology - Generalist
For the complete procedure on how to define filters, see Creating or modifying filter rules.
When the selection is complete, click Generate.
RAC/M Identity will browse its repository and build roles by mining the identities and assets that match the selected filters and settings.

Click on the Click here to reach the role list panel link located in the green band at the top of the screen to complete the role definition.
This action opens the page that allows you to complete, edit and review the newly created roles.
The roles are created and added to the modeling session. You can continue to refine the roles until they are satisfactory.
For more information on editing and reviewing roles, see Editing a Role.
Creating an empty role
This button allows you to add an empty role to a role modeling session. An "empty" role is essentially a shell role that you can add to later. The role will be created with just its name.
This approach is useful for creating roles that will be modeled manually, without mining.
To add an empty role:
If you have just created a role modeling session, go directly to step 4.
On the menu bar, click ACCES> Role Modeling Sessions.
Select the modeling session to which you want to add roles.
To the right of the Role mining section, click the
button.
Click on the Empty Role button. In the Role Name text box, type the name of the role.
Click on Generate.
Click the Click here to edit this role link located in the green band at the top of the screen to complete the role definition.
This action opens the page that allows you to complete, edit and revise the newly created role.
For more information on editing and revising roles, see Editing a Role.
Creating a new role from a template
You can create a new role from a template role.
Note
The name of the new role will be created from the name of the template role followed by a unique number. You can rename the role and adjust the description and all parameters as you wish.
To duplicate a role:
Click on ACCES> Role Versions.
In the list, select the role you want to duplicate
Click on the Clone Role button.
The Role Edit page will open on the Details tab.
Adjust the settings for the new role and click Save at the bottom of the page.
A new role will be created. The name will be constructed from the name of the sample role and a unique, automatically generated number to distinguish it.
See Editing a role for more details.
Creating a new role version by mining
You can mine an existing role with different parameters, which will automatically create a new version of the role and add it to the modeling session.
To create a new version by mining:
If you have just created a role modeling session, go directly to step 4.
On the ACCES menu, click Role Modeling Sessions.
Select the desired session from the list.
The Role Modeling page will open on the Details tab.
To the right of the Role Mining section, click the
button.
Click on Existing Role.
Select a role from the Select Role list.
You can use the Starts with and End with checkboxes to refine the search.
In the Entitlement inclusion treshold field, enter a percentage. This percentage determines the percentage of identities, from the selected population, that must have a specific entitlement in order for it to be included in the role.
See Creating a new role by mining for more details on the Inclusion threshold.
Check one of the buttons to determine how directly assigned members will be assigned.
Check Assign members directly based on mining criteria to directly assign identities that meet the asset filtering criteria.
Note
This option uses the existing role assignment rule to identify the identities to directly assign to the role, i.e. once assigned they will remain so unless manually removed.
Check Do not assign any members directly if no directly assigned member should be automatically assigned.
Check Keep existing directly assigned members so that the existing directly assigned members of the role are preserved.
Check the Include Inactive Accounts box if you want the role drill down to take into account inactive accounts and associated access.
Scope
In the Criteria: Filters dialog box, in the lists, select the filter type and validate or edit the rules.
For the complete procedure on how to define filters, see Creating or modifying filter rules.
Under Variable Attributes for Multiple Role Creation, next to Identity, click the Edit button.
For the complete procedure on how to define filters, see Creating or Modifying Filter Rules.
When the selection is complete, click Generate.

RAC/M Identity crawls its repository and builds roles by mining identities and assets that match the selected filters and parameters.

Click the Click here to edit this role link located in the green band at the top of the screen to complete the role definition.
This action opens the Details page which allows you to complete, edit and review newly created roles.
The roles are created and added to the modeling session. You can continue to refine the roles until they are satisfactory.
For more information on editing and revising roles, see Editing a Role version.
Creating a new role version from a template
You can create a new version of a role independently of a modeling session from an existing role version.
To create a new version from a template:
On the ACCES menu, click Roles or Role Versions.
Select the role version to duplicate.
The role editing page will open on the Details tab.Click the Clone Role Version button at the bottom of the page.
The role edit page will open on the Details tab.
Adjust the parameters for the new role version and click Save at the bottom of the page.
A new role version will be created and added to the role. A unique number to distinguish it will be automatically generated and associated with the version.
See Editing a Role for more details.
Editing a role version
You can make changes to a role at any time either to refine a role version or to evolve it to reflect changes in your organization.
See also
To edit a role version:
On the ACCES menu, click Roles or Role Versions.
Select the role version to edit or revise.The role editing page will open on the Details tab.

Note
If the role version is active, very few fields can be modified.
Besides the name and description, only directly assigned members and the availability of the role in the self-service portal can be changed.
To change other fields such as assignment rules, you must first disable the role version.
Caution
To modify a role version without affecting the operation, you have to create another role version.
See Creating a new role version for details.
Make the required changes as follows:
Name
Adjust the role name if required.
Description
Adjust the description of the role if required.
Role version
The list displays the different versions of this role. You can select a new version of the role if desired.
The status of the selected version as well as the last activation and deactivation date and time are displayed.
Description of changes in this version
This field is automatically initialized with the content of the Description field. It can be edited as desired to reflect changes that will be made to the role version.
Role Modeling Sessions
Displays the role modeling sessions that include this role version. You can click a modeling session to open it.
Assignment Criteria
If the role version is Inactive, you can click the Edit button to edit the filter rules used to assign the role.
Note
These rules are used to automatically assign the role to identities that match the criteria.
These rules are initialized to the value of the identity filter rules used during mining if the role was mined.
Role available in self-service
Check one of the two boxes below to set the availability of this role in the self-service portal request pages:
- Can be requested in an access request
- Can be added to a role modification request
Approvers
It is possible to configure approvals for identity access requests and role modification requests.
For each of the following approval levels, indicate if the level is required and complete the required information, if applicable.
Identity Approver Approval Required
For access requests, check this box if the manager of the person requesting access must approve the assignment of this role.
For role requests, check this box if the manager of the directly modified members in the request must approve the change of identity within this role.
In both cases, the Approver Group defined at the identity level will be used.
Role Owner Approval Required
Check this box if the role owner, represented by its delegation group, must approve the role assignment.
Special Approval
Select the checkbox if a third level of approval is required to assign this role.
If a delegation group other than the identity or role owner group must approve the request, select it from the drop-down list.
Note
Delegation groups must be created beforehand. See Create a delegation group
Groups
If the role version is Inactive, this section allows you to manually add or remove groups from the role. If the version is Active you will only be able to view the groups included in the role.
The groups included in this version of the role are displayed in the list on the right. You can remove them using the buttons on the right.
You can open the details page of a selected group by clicking on the
.

To add groups to the role:
Select an asset from the Asset drop-down list. The groups associated with that asset will appear in the Available list.
You can also search for groups in the existing set of groups by using the Search for Group field.Select one or more groups from the Available list.
Use the
arrow to add them to the role.
You can use the
to open the group.
Access rights
If the role version is Inactive, this section allows you to manually add or remove access rights to the role. If the version is Active you will only be able to view the access rights included in the role.
Access rights are permissions that can be associated with items associated with assets that are different from groups.
Example
Permissions associated with directories and files on *NIX systems are represented by access rights.

To add access rights to the role:
Select an asset from the Asset drop-down list. The access rights associated with that asset will display in the Available list.
You can also search for access rights in the existing set of access rights by using the Search for Access field. Select one or more access rights from the Available list. Use the
arrow to add them to the role. You can use the
to open the access right.
Directly assigned members
If you are using a hybrid role template (see - About Roles), you can add members to the role manually, regardless of the assignment rules that apply to automatically assigned members.
The identities to which the role has been assigned are displayed in the list on the right. You can remove them using the buttons on the right.
You can open the details page of a selected identity by clicking on the
.

To add members directly:
In the Search for Identity text box, type a few letters of the name of the identity you are looking for. In the list of available identities, select the desired identity and click the arrow to move it to the Selected list.
Automatically assigned members
This section displays all identities that are assigned the role automatically according to the assignment rules you have defined.

If the role version is active, you can click on one of the members to display the revision tab to view the role assignment for the selected member.
Note
If the role version is not active, the revision tab will not contain any information.

Include Roles
This section allows you to include roles to the current role. Directly and automatically assigned members of the current role will also receive the groups and access rights associated with the included roles.
See About Group and Role Hierarchies for details.
The included roles are displayed in the list on the right. You can remove them using the buttons on the right.
You can open the details page of a selected role by clicking on the
.

To add included roles:
In the Role Search text box, type a few letters of the name of the role you are looking for. From the list of available roles, select the desired role and click the arrow to move it to the Selected list.
Click Save to save the changes to the role.
Reviewing a Role version
You can review the settings of an active role version as well as the assignment of the role to directly and automatically assigned members.
To review a role version
If you are already editing a role, go directly to step 3.
On the ACCES menu, click Roles or Role Versions.
Select the role version you want to review.
The role editing page will open on the Details tab.
Click on the Revision tab.

Note
If the role version is not active, the revision tab will not contain any information.
Role version
The list displays the different versions of this role. Select the version of the role to be reviewed.
The Role Information section displays detailed information about this role version.
Membership
The Membership section displays the effect of the role on its members.
You can view, for each member, the groups and access rights they hold in relation to the role's content. Accesses held in agreement with the role are displayed in green, accesses held in excess of the role are displayed in red while accesses that are part of the role but not held by the member are displayed in blue.
Select a member from the drop-down list to view their accesses.
The Filter Groups with Role Criteria checkbox allows you to filter the assets scanned to prevent accesses associated with assets that do not match the role from appearing in the lists as excess accesses.
The box is checked by default and is the recommended choice.
Example
An identity has access to office applications and business applications whose accesses are managed by different roles. If we review the office role and the box is not checked, the accesses related to the business applications will appear as excess accesses in red.
At the end of the review, if the role configuration is satisfactory, go back to the Details tab and click on the Enable button to make the role effective.
See also
Note
Make sure the last changes were saved by clicking the Save button.
Activating one or more role versions
Specific versions of roles can be activated individually or in combination.
To activate a single role version:
- On the ACCES menu, click Roles or Role Versions.
Select the role version you want to activate.
The Role Edit page will open on the Details tab. - Click the Activate button at the bottom of the page. A window will open for the activation options.
- Choose whether provisioning should be performed during activation or not.
- Click the Activate button at the bottom of the window.
To activate multiple role versions:
On the ACCES menu, click Role Modeling Sessions. Select the desired session from the list.
The Role Modeling page will open on the Details tab.In the Roles section, ensure that all roles you want to activate are in the Selected Roles list.
At the top of the page, click the Enable button.
Note
If all the roles you want to activate are not in the list of selected roles, you can add them either by creating the missing roles or by adding existing roles.
See also Assigning Roles to a Modeling Session for details.
Deleting a role version
To delete a role version:
Click ACCESS> Role Versions.
From the list, select the role version you want to delete
Click on the
button.
Note
Role versions must be inactive to be deleted. Active role versions cannot be deleted.
About Segregation of Duties
Segregation Of Suty (SOD) rules are determined by organizational policies. RAC/M Identity allows you to define and enforce these rules.
Task segregation rules are validated in several circumstances. The indicator business logic periodically analyzes the repository for anomalies and high risk situations, including SOD rule violations. In this case, violations are reported by indicators and buttons are used to navigate directly to the problematic situations in order to resolve them quickly.
SOD rules are also validated during access review campaigns. Violations can be included in access review campaigns. Violations can also be documented in standard and customized reports.
As a preventive measure, SOD rules are also validated during access requests issued from the self-service portal. If a request contains entitlements that would cause a violation, the request is automatically routed to a designated stakeholder, or their delegation group, to resolve the conflict.
In this case, the request can be conditionally ou unconditionnaly accepted, rejected or modified as appropriate.
RAC/M Identity allows you to define the nature of task segregation rules by defining exclusion rules on five types of objects and attributes:
- Asset: For example, the organization does not allow anyone to have an account in the order entry application and the order fulfillment application.
- Group: For example, a member of an Active Directory group representing external contractors cannot be a member of a group representing managers.
- Role: For example, a member of the Manager role must not also have the Union Representative role.
- Organizational Structure: For example, an identity assigned to the Accounts Receivable department must not also be assigned to the Audit department.
- Title: For example, an identity with the title of Nurse cannot also hold the title of Cardiologist.
Note
RAC/M Identity analyzes the accesses held by all identities associated with a person to detect violations of separation of duties rules.
That is, a person associated with multiple identities cannot hold accesses that would violate separation of duties rules, even if the conflicting accesses are assigned to separate identities.
This section presents the steps for creating one or more segregation of duties rules as well as viewing and editing them.
Creating a Segregation Of Duty rule
To create a Segregation Of Duty rule:
On the ACCES menu, click Task Segregation. The Task Segregation page opens with a list of existing rules related to assets.

Select the type of rule to create by clicking on the desired tab (Asset, Group, Role, Organizational Structure or Title).
Click on the Definition tab.
At the top right of the page, click on the
button. In the Name text box, enter the name of the rule. In the Description text box, enter a description of this rule. In the Approval Group text box, double-click to open the list or enter the name of a delegation group. This is the delegation group that will be responsible for reviewing this access segregation rule. In the two Mutually Excluded Items boxes (the excluded item depends on the tab selected in step 2.), double-click to open the list or type in the name of the items that should be mutually excluded.
Click Save.
The rule is now available on the Task Segregation selection page, in the list of the selected category tab (Role tab in our example).

Segregation of Duties selection page, list of rules associated with roles
To edit the rule configuration, in the list, click the rule to open its Details page.
Editing a Segregation Of Duty rule
To modify a Segregation Of Duty rule
In the ACCESS menu, click on Segregation of Duties. The Segregation of Duties page opens with a list of rules related to assets.
Select the type of rule you want to modify by clicking on the desired tab (Asset, Group, Role, Organizational Structure or Title).
Click on the desired rule to open its details page. Make the desired changes
Click Save at the bottom of the page to save your changes.
Generating multiple Segregation Of Duty Rules
To generate multiple Segregation Of Duty Rules
On the Segregation of Duties details page, click the Generation tab.
Click the tab of the category for which you want to create rules (see Step 3. of Creating a Segregation of Duty Rule.

Segregation of Duty details page, multiple rule generation
In the Role list (in our example), click on the arrow or type in the name to open the list, and select the role from which other segregation rules will be created.
In the Name text box, type the name that will be used as a prefix for all rules.
In the Description text box, enter the reason for these rules.
In the Reviewer text box, enter the name of the delegation group responsible for reviewing the rules.
Under Exclude, in the Roles to Exclude list (in our example), enter the name or click on the magnifying glass to open the list and select the roles that should be excluded from the role you selected as the "Item to Isolate".
In the list on the left, select the roles and click on the arrow to move them to the list on the right.

Segregation of Duty details page, selection of excluded items
Click Generate.
The rules are available in the Segregation of Duties Details page, in the list of the selected category tab (Role tab in our example).

The Segregation of Duty selection page, list of rules related to roles
To modify the configuration of a rule, in the list, click on the rule to open it.
Creating a Business Function
An business function is a simple mechanism to reflect additional or complementary responsibilities to those corresponding to a person's roles in the company. For example, an individual may be assigned the responsibilities of "Team Leader - Development" for a specific or indefinite period of time. This chapter presents the procedure for creating an business function.
To create a business function:
On the ACCESS menu, click Business Functions.
At the top right of the page, click the
button.
On the Business Functions Details page, in the Name text box, type the name of the identity.

In the Description text box, type a description of the function.
In the External Object ID text box, enter a unique identifier for the new additional function. This identifier is a technical name that must be unique and permanent.
Click Save
The additional function can be added to an identity and used by business logic to assign roles dynamically or as a filter parameter.
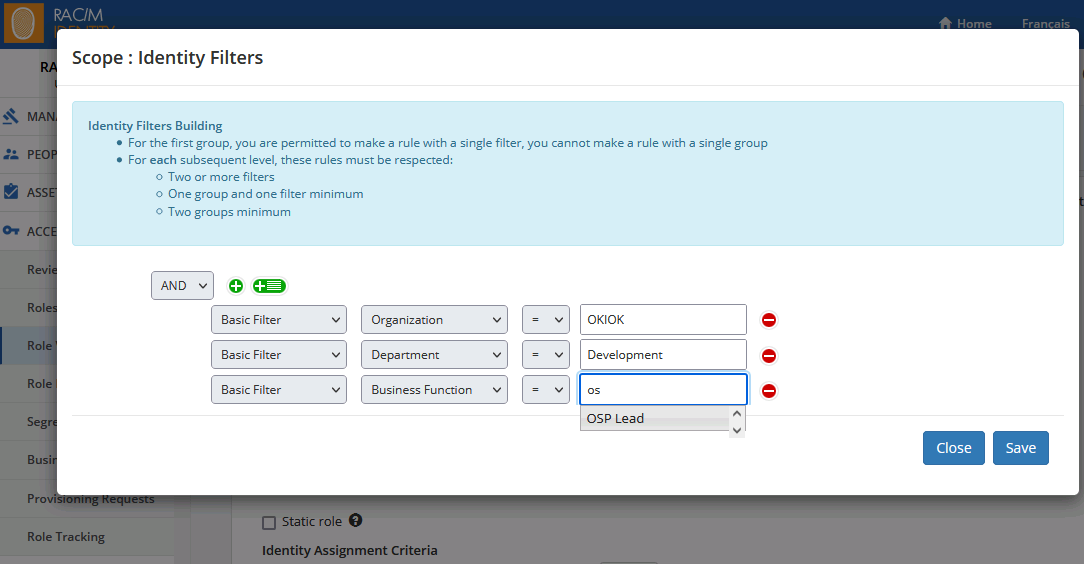
About the organization
About Provisioning
This section describes how to track the progress of provisionning workflows, tasks, and queries resulting from requests from the self-service portal or other sources.
The various screens allow you to view the status of requests and sub-requests, diagnose potential problems and remedy them if necessary.
You can view the status of queries by:
- Tasks, to view approval or manual create/remove/edit tasks
- Identity Requests, to view access requests made through the self-service portal
- Identities, to view requests for identities
- Roles, to view requests for roles
- Accounts, to view requests for accounts
- Groups, to view requests to add or remove groups
- Written requests, to view requests made in free fields in the self-service portal
- Role Requests, to view role requests made through the self-service portal
In each screen, you can click on the links to navigate the chain of related queries and subqueries.
All screens display similar information, but the fields displayed vary depending on the nature of the list.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Request | Automatically Generated Query Number |
| Identity | Identity associated with the query |
| Role | Role associated with the query |
| Asset | Asset that is the subject of the query |
| Account | Account associated with the query |
| Group | Group to be added or removed by the query |
| Type | Type of query or subquery Add, Remove, Change |
| Status | Query status Pending, Provisioned, Completed, Completed (closed) |
| Comment | Detailed information about the request |
| Description | Additional information if available |
| Date request created | Date request created |
| Approval | Approval Status Pending, Approved, Rejected |
Note
For access requests, the status of the requests will change from Completed to Completed (closed) once the requested changes are detected in the target systems, which confirms that the request is completed correctly.
The possible values of the query types, states and approval states may change over time. The values shown in the table are for informational purposes only.
To view the progress of current queries:
In the PROVISIONNING menu, click on the type of requests you want to view. The list of current queries is displayed.

You can filter the list of queries to show only queries with errors for example, or filter on any other keyword using the search box on the right of the screen.
Click on the hyperlinks to navigate through the chain of queries and subqueries and open the details page.

About Reports
This section describes how to generate standard, custom, and anomaly reports.
Note
For access review campaigns, the reports are generated within the activity, refer to Starting and Tracking a Review Campaign.
In addition, you can use data visualization tools such as Tableau, PowerBI and others to generate reports and produce customized dashboards and indicators.
Generating Standard Reports
RAC/M Identity offers several standard reports.
To generate standard reports:
In the REPORTS menu, click Reports.
In the Reports list, select the type of report you want to generate. A description of the report appears in the Description text box. Depending on your choice of report, different text boxes and lists become available.

Click Generate Report.
The report appears as a PDF and an Excel file in the list on the right. If the list is long, type a key word in the List Filter text box.

Click the PDF file to view it in your browser or click the Excel file to download it to your workstation.
Using Custom Reports
If none of the standard reports meet your needs, you can create custom reports using the JasperReport format via the iReport Designer tool.
Important
For your custom report to appear in the RAC/M interface, they must be created using the JasperReport format.
To create custom reports, you must have a basic knowledge of SQL and query syntax. You must also have access to the RAC/M repository and it is strongle recommended that you use an SQL script generator to test your queries before using them in the Query Text dialog box of iReport Designer.
RAC/M Identity also allows you to add fields to the Reports page. These are used as additional criteria when generating the custom report. These fields can be:
- A drop-down list: A drop-down list is created if the field gets its data either from the
Application_IDcolumn or theApplication_Group_IDcolumn. - A text box: A text box is created if the field gets its data from any other column.
For a field to appear in the RAC/M interface, make sure that Use as prompt is selected in the field parameters.
For more information on iReport Designer or JasperReport, please refer to their respective documentation.
To generate a custom report:
On the REPORTS menu, click Reports.
In the Reports list, select Custom Report.
In the Custom Report list, select your custom report. Depending on your choice of report, different text boxes and lists become available.
Click Generate Report.
The report appears as a PDF and an Excel file in the list on the right. If the list is long, type a key word in the List Filter text box.
Click the PDF file to view it in your browser or click the Excel file to download it to your workstation.
Generating Anomaly Reports
The list of standard reports includes reports that can be used to examine anomalies. The following are examples of reports to use to find anomalies:
- Accounts Associated with an Identity with Different Name
- Accounts of Identities Terminated between Two Dates
- Identities Associated with a Person with Different Date of Birth
- Identities Associated with a Person with Different Name
- Identities Logged after Termination Date
- Identities with Multiple Accounts in a Given Asset
- Identities with Supervisor in Different Departments
- Identities without Supervisor
- Identity Discrepancies
- Identity Terminated between Two Dates
- Etc.
These reports are generated the same way as standard reports (see Generating Standard Reports).
About RAC/M Identity configuration
RAC/M Identity is designed to be extremely flexible and capable of adapting to the business and technological contexts of all organizations, whether they are very small or very large, without programming, by simple configuration. This is the Low-Code/No-Code approach.
This section describes how to configure RAC/M Identity and the modules and policies that make up the business logic required to implement the desired automated processing.
Important
The following procedures are used to define and modify the business logic of your IAM service. They require a good understanding of how RAC/M Identity works and of your technological environment and are usually performed by the solution's architects, integrators or technical experts.
Incorrect configuration could result in a malfunction of the IAM service.
Note
You can view the modules, blocks and sequences included with RAC/M Identity to better understand how to configure modules and build blocks and sequences.
See also the Technical Reference Guide for more information.
To this end, the CONFIGURATION function in the main menu allows you to:
- View and edit RAC/M Identity configuration files
- Create, modify, duplicate and delete functional blocks (File Managers, Formers, Collectors, Extractors, Modules)
- Create, modify, duplicate and delete Blocks and Sequences.
- Create, modify and delete Mappings.
- Create, modify and delete manual provisioning strategies
- Create, modify and delete ICF connectors.
- Create, edit and delete Policies (account, username and password)
- View and edit email notifications
While configuration of the modules differs according to their nature, updating, exporting, importing, duplicating and deleting them is the same.
In addition, the modules can be run directly by clicking on the Execute button. The results can be viewed in the MANAGE menu under Sequence Execution.
In order to lighten the text, only the detailed instructions for the creation of modules will be provided, the other operations being similar.
For more information on these common tasks, see Basic Tasks.
Viewing or Editing a Configuration File
To view or edit a configuration file:
On the CONFIGURATION menu, click Configuration Files.
From the list, select the file you want to view or edit. You can navigate to the beginning or end of the file using the buttons at the top right.
You can view the file in raw format by clicking on the
button.
Make the required changes to the file.
Click Save to save your changes.
Note
You must have the required permissions in your RAC/M Identity profile to edit a configuration file.
See Permission Reference of RAC/M Identity Profiles for more information.
The RAC/M Identity service must be restarted for your changes to take effect.
Creating a File Manager
File managers are used to transfer files between RAC/M Identity and servers, such as FTP sites. They can use different transfer protocols, such as FTPS, SFTP or SCP, and different authentication mechanisms.
In general, primitives whose name contains the word External are used to transfer files between an external server and your RAC/M Identity instance, while primitives whose name contains the word Local are used to manipulate files on the local file system of your RAC/M Identity instance.
The other primitives are used to perform specific processing, see the primitives description or consult the Technical Reference Guide for more details.
To create a file manager:
On the CONFIGURATION menu, click File Managers. The File Managers page opens.

At the top right of the page, click the
button.
Under Details, in the Name text box, type the name of this new file manager.
The name should be distinctive as it will appear in a list of file managers.
In the Source File text box, type the path to the source file.
In the Result File text box, enter the path to the file where the data will be dropped. In general, files must be dropped into the RAC/M Identity working directories to be processed.
In the Error File text box, enter the path to the error file. Leave blank to use the default error file.
In the Description text box, enter a description of what this handler is used for.
Under Behavior on error click on the desired option:
- Stop Processing to stop the processing sequence.
- Skip remaining operations... to stop processing the current block and continue with the next block
- Continue with the next operation to continue processing
Under Primitive, in the Name list, select the primitive you want this manager to use. For a detailed description of the primitivees, see the Technical Reference Guide.
If you selected an primitive whose name includes the word External, such as ModuleExternalSCPGet, ModuleExternalSCPPut, ModuleExternalSFTPMove, or ModuleExternalSFTPMoveArchive, you need to complete the information under Connection.
Field Description Host Type the address of the server host Port Type the port you need to use to connect to the server. Account Type the username used to log in on the server. Password Type the password used to log in on the server. Private Key Type the private key used by the server. You will have generated this key using a third-party application. Public Key Type the public key used to connect to the server. You will have generated this key using a third-party application. Test button Click this button to test the connection. If you selected an primitive such as ModuleIdentityEventHandler or ModuleProfileEventHandler, you need to complete the information under Event Tables.
Field Description Target Event Table Select the RAC/M table into which data is sent. Source Event Table Select the Staging table from which data is obtained. Under DATA MAPPING, enter in which fields and how the information should be deposited.
At the bottom of the page, click the Save button.
The BLOCK ASSOCIATION section displays the list of sequences and blocks in which this file manager is used. The list is empty when the file manager is first created.
Creating a Formatter
Formatters are used to correct or transform data in CSV files. For example, formatters can be used to decode fields encoded in BASE 64 or HEX, repair and harmonize date formats, manipulate, add or remove columns.
In general, formatters process a CSV source file as input and create a CSV result file as output. Formatters can also be used to convert flat files to CSV format so that they can be processed by RAC/M Identity.
Example
Formatters can be used to split the first and last name of an identity into two columns when the data source contains the full name in a single column.
To create a formatter:
On the CONFIGURATION menu, click Formatters. The Formatters page opens.
At the top right of the page, click the
button.
Under Details, in the Name text box, type the name of this new formatter. The name should be distinctive as it will appear in a list of file formatters.
In the Description text box, type a description of what this formatter is used for.
In the Error File text box, type the path to where you want to save the error file. Leave empty to use the default error file.
In the Separator text box, type kind of separator you want to use (for example, ":", "|", ";", etc.).
In the Nb Column text box, type the number of columns you expect to be in the CSV file. This will serve as a validation before processing the file.
In the File encoding field, enter the encoding type corresponding to the source file. UTF-8 and ISO-8859-1 for .XLSX files are the most frequently used
Under Behaviour in case of errors click on the desired option:
- Stop the sequence to stop the processing sequence
- Skip remaining operations... to stop processing the current block and continue with the next block
- Continue with next operation to continue processing
Under Primitive, in the Name list, select the name of the primitive to be used.
Primitives whose names contain the words ToCSV are used to convert LDIF, XLS, XLSX or other files into CSV format so that they can be processed by RAC/M Identity.
For a detailed description of the primitives, see the Technical Reference Guide.
Under File Selection, in the Source CSV File text box, enter the path and name of the file to process.
In the Type drop-down list, select the type of file to process or leave it at Automatically detect to let RAC/M Identity automatically determine the type of file to process.
In the Result File text box, enter the path and name of the CSV file that will contain the formatting result.
Note
The path of the source and result CSV files must be relative to the RAC/M Identity working directory, as defined by the path.source.csv property in the config.properties file.
In the Header Type list select either Header or Index. Header will display the name of the columns while Index will display the number of the columns in the DATA MAPPING section below.
In the Source Template File list, select the template file, if one is available, that corresponds to the file to be processed.
If a template file is selected, the header type selection applies to the template file rather than the source file.
Note
Template files must contain at least one line. If the template file contains column headers, they can be used to identify the columns in the DATA MAPPING section.
Template files must have the word template in their name to be recognized as template files, must be of the same type as the source file to be processed, such as .XLSX or .CSV. and must be dropped into the RAC/M Identity working directory or a sub-directory.
Example: GRA-template.csv
Click the Save button before proceeding with the next steps.
In the Source Template File list, if source file uses a predefined template, select the template.
Click the Load Column Headings from Tables button.
The DATA MAPPING section is displayed.

In the Regular expression list, in the text box next to the source column that needs to be formatted, enter the parameters required by the selected primitive.
Example
If you use a primitive to remove a string such as the prefix TH- from the content of a column, you must enter TH- in the Regular expression text box next to the column in question.
Note
The parameters that can be used vary depending on the Primitive you have selected. For more information on primitives and their parameters, see the Technical Reference Guide.
Click Update.
The formatter is created.
Creating a Collector
The collector is used to transfer data from a CSV files or from a Data source via an ICF connector to a RAC/M repository staging table.
Collectors can be grouped with other types of modules to create blocks.
Collector for a CSV File
RAC/M offers ready-made modules to work with CSV files:
- ModuleCSVUpdateOrInsertTable
- ModuleCSVUpdateTable
- ModuleCopyCSVToTable
To create a collector to import data from a CSV file:
On the Menu Bar, click CONFIGURATION> Collector.
At the top right of the page, click the
button.
Under Details, in the Name text box, type the name of the collector.
In the Description text box, type the description of what the collector is used for.
In the Result File and Error File text boxes, type the path to the directory where the result (.log file) of the data importation will be found and the path to the directory for the error file (.log file).
In the Separator text box, type the separator used in the CSV file.
The semicolon ( ; ) is the default value.
In the File Encoding text box, type the encoding used if it is not UTF8.
Select how you want the sequence to proceed if an error occurs using this module.
At the bottom of the page, click the Save button.
The collector is added to the Name list on the Collectors Details page.

Under Primitive, in the Name list select an importation module.
You can use a ready-made module or one you have configured yourself (refer to Configuring a Module. For our example, select ModuleCopyCSVToTable.

Under Data Import enter the information as follows:
Target table
In the list, select the staging table into which you want to import the data. For our example, IDENTITY_IMPORT. (For more information about staging tables refer to Description of the Staging Tables.)
Source file
In the list, select the CSV file you want to import. For our example /RH/*.csv.
Source Template File
If your source file uses a predefined template, select it. For our example RH/gabarit/template_employes.
Column Header Type
In the list, select Header to populate the table using the header name or Index using the index number. For our example, Header.
a) At the bottom of the page, click Update.
b) Click the Load columns from table and CSV files button.
You can now map the imported data to the RAC/M table in the Data Mapping section.
Under Data Mapping match data according to the following parameters: For our example, the rows under Target Table Column have been imported from the
Identity_Imorttable.Target Table Column
These values represent the column headings of the RAC/M table. You can add a column of the same name by clicking the
button. This allows you to concatenate multiple columns in the sources file. For example, the RAC/M HR_Department_ID column could take its value from both the Hospital and Department columns in the source file; which you would separate using a hyphen.

Data Source Type
In this list you select what will be the type of data that will populate the column.
- Constant: Mapping will use the value you specify in the Constant/Value text box. For example, the HR_Work_Location_Name column could always be “Downtown Office”.
- Date: Mapping will use the date format you specify in the Format text box. The date is taken from the selection made in the Source Column list. Make sure that you match the date formats. For example, the Hire_Date_Str column could display the date that was entered in the “Hire date” column of the source file.
- Cur_User: Mapping will use the user you specify in the Constant/Value text box.
- Column: Mapping will use the selection made in the Source Column list.
- Column_with_Default: Mapping will use the content directly from the source (column, file, or connector). If nothing is found, the value in the Constant/Value text box is used instead.
- Cur_Time: Mapping will use the current time as the value.
- File_Name: Imports the name of file selected in the Source File list in the Data Import section.
- Column-Hashed: The value is hashed to fit the space allowed in the table.
- Column_Mask: Part of the value is masked using an expression defined in the Constant text box. For example, for a source value of 00430022887, you will obtain *******2887 if you use the following mask: ^d(7)[a-zA-Z0-9] or 0043002**** if you use: [a-zA-Z0-9].{3}$.
Source Column
In the list, select the name of the column in the source table from which you want to import the data.
Constant/Value
If you have selected Constant or Column_With_Default as the data source type, type the value to use in this text box.
Format
If the source type uses a specific format, type it in this text box; if not, leave the box empty. For example, a date could have the yyyy-mm-dd string.
Unique
Select this check box if the value must be unique.
Click Update.
Collector for an ICF Connector
RAC/M offers ready-made modules to work with ICF connectors:
- ModuleICFAccountProvisionning
- ModuleICFIdentityProvisionning
- ModuleICFImportData
- ModuleICFProfileProvisionning
To configure a collector to import data from an ICF connector:
On the Menu Bar, click CONFIGURATION> Collector.
At the top right of the page, click the
button.
Under Details, in the Name text box, type the name of the collector.
In the Description text box, type the description of what the collector is used for.
In the Result File and Error File text boxes, type the path to the directory where the result (.log file) of the data importation will be found and the path to the directory for the error file (.log file).
In the Separator text box, type the separator used in the CSV file.
The semicolon ( ; ) is the default value.
In the File Encoding text box, type the encoding used if it is not UTF8.
Select how you want the sequence to proceed if an error occurs using this module.
At the bottom of the page, click the Save button. The collector is added to the Name list on the Collectors Details page.
Under Primitive, in the Name list select an importation module.
You can use a ready-made module or one you have configured yourself (refer to Configuring a Module. For our example, select ModuleICFImportData.

Depending on your choice of module, different importation options are available.
- Under Data Import, enter the required information as follows: The available settings differ depending on your chose of importation module.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| RAC/M Table | In the list, select the staging table into which you want to import the data. For our example, select Application_Account_Import. |
| ICF Connector | In the list, select the ICF connector (refer to Configuring an ICF Connector. |
| Object Class | In the list, select the object class you want to use. The selection depends on the selected ICF connector. For our example, select Account. |
| Load Columns from Table | Clicking this button opens the Data Mapping section which you used to map source data to the table format. |
| Load Attributes from Target System | Clicking this button imports data into the Target System Attribute list. |
Under Data Mapping match data according to the following parameters:
Rack/M Column
These values represent the column headings of the RAC/M table. You can add a column of the same name by clicking the
button. This allows you to concatenate multiple columns in the sources file. For example, the RAC/M HR_Department_ID column could take its value from both the Hospital and Department columns in the source file; which you would separate using a hyphen.

Data Source Type
In this list you select what will be the type of data that will populate the column.
- Constant: Mapping will use the value you specifiy in the Constant/Value text box. For example, the HR_Work_Location_Name column could always be “Downtown Office”.
- Date: Mapping will use the date format you specify in the Format text box. The date is taken from the selection made in the Source Column list. Make sure that you match the date formats. For example, the Hire_Date_Str column could display the date that was entered in the “Hire date” column of the source file.
- Cur_User: Mapping will use the user you specify in the Constant/Value text box.
- Column: Mapping will use the selection made in the Source Column list. For our example, for Account_Name select Column.
- Column_with_Default: Mapping will use the content directly from the source (column, file, or connector). If nothing is found, the value in the Constant/Value text box is used instead.
- Cur_Time: Mapping will use the current time as the value.
- File_Name: Imports the name of file selected in the Source File list in the Data Import section.
Target System Attribute
In the list, select the name of the column in the source table from which you want to import the data. The elements in the list were imported from the server connected to the selected ICF connector when you clicked the Load Attribute from Target System button.
Constant/Value
If you have selected Constant or Column_With_Default as the data source type, type the value to use in this text box.
Format
If the source type uses a specific format, type it in this text box; if not, leave the box empty. For our example, type how the date is entered in the source file (it could be yyyy-mm-dd).
Unique
Select this check box if the value must be unique.
Click Update.
Configuring an Extractor
Extractors are used to extract data from the RAC/M Identity and access repository and store it in a standard format (for example, a CSV file).
To configure an extractor:
On the Menu Bar, click CONFIGURATION> Extractor.
At the top right of the page, click the
button.
Under Details, in the Name text box, type the name of this new extractor. The name should be distinctive as it will appear in a list of extractors.
In the Description text box, type a description of what this extractor is used for.
In the Error File text box, type the path to where you want to save the error file.
In the Separator text box, type kind of separator you want to use (for example, : (colon), | (pipe), ; (semicolon), etc.).
In the File Encoding text box, if you want the file to be encoded, type the encoding type.
Under Behavior in case of errors, elect the way you want RAC/M to respond when an extraction error occurs.
At the bottom of the page, click the Save button.
Under Primitive, in the Name list select an extraction module.
For our example, select ModuleTableToCSV.

- Under Data Import, enter the required information as follows:
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Target File | In the list, select the file in which you want to import the data from the CSV file. |
| Source Table | In the list, select the RAC/M table from which you want the data to be extracted. For our example, Identification. |
| Template File | In the list, select the template file you will use to generate the resulting file. The Data Mapping zone will only be available if a template is selected. For our example, RH/gabarit/template_employes.xlxs. |
| Column Header Type | In the list, select Header to populate the table using the header name or Index using the index number. For our example, Header. |
- Click Update.
- Click the Load table columns from CSV button to populate the data mapping zone.
- Use the Criteria section to add filters to the extraction.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Criteria Column | In the list, select the criteria you want to use as a filter. |
| Operation | In the text box, type “=” if you want the filter to equal a specific value. |
| Value | In the text box, type the value of the filter. If you type text (or a string), make sure to use single quotation around it (for example, ‘Nurse’). You can use an SQL query format to enter more advanced values. |
To add a filter, click the **Add** button.
Under Data Mapping, match data according to the following parameters:
Rack/M Column
These values represent the column headings of the RAC/M table. You can add a column of the same name by clicking the
button. This allows you to concatenate multiple columns in the sources file. For example, the RAC/M HR_Department_ID column could take its value from both the Hospital and Department columns in the source file; which you would separate using a hyphen.

Data Source Type
In this list you select what will be the type of data that will populate the column.
- Constant: Mapping will use the value you specify in the Constant/Value text box. For example, the HR_Work_Location_Name column could always be “Downtown Office”.
- Date: Mapping will use the date format you specify in the Format text box. The date is taken selection in the Source Column list. Make sure that you match the date formats. For example, the Hire_Date_Str column could display the date that was entered in the “Hire date” column of the source file.
- Cur_User: Mapping will use the user you specify in the value. Constant/Value text box.
- Column: Mapping will use the selection made in the Source Column list. For our example, for Account_Name select Column.
- Column_with_Default: Mapping will use the content directly from the source (column, file, or connector). If nothing is found, the value in the Constant/Value text box is used instead.
- Cur_Time: Mapping will use the current time as the value.
- File_Name: Mapping will use the name of the source file as the value.
Source Column
In the list, select the name of the column in the source table from which you want to import the data. If you select a column with the “_ID” suffix, the
icon appears, enabling you to browse the RAC/M repository and find the precise column you want to use. When you click the icon the target table opens in a dialog box. Click a column to select it. To browse to a secondary table, click that same icon next to the “_ID” column that links to the secondary table.
Constant/Value
If you have selected Constant or Column_With_Default as the data source type, type the value to use in this text box.
Format
If the source type uses a specific format, type it in this text box; if not, leave the box empty. For example, a date could have the yyyy-mm-dd string.
Unique
Select this check box if the value must be unique.
Configuring a Module
Each module corresponds to one of the organization’s business logic, which is a basic process used to manipulate data within the Identity and access repository. The most common module takes the data from the staging table and transfers it into the RAC/M table.
Example
To copy the data from the Identity_Import table into the Identification table, you would use the IdentificationCopy module.
Modules can then be grouped together to create blocks.
For a complete list of predefined modules and primitivees, refer to the Technical Reference Guide.
To configure a module:
- On the CONFIGURATION menu, click Modules.
- At the top right of the page, click the
button.
- Enter the required information as follows:
- a) Under Details:
Name
Type the name you want to give to the module. The name should be distinctive as it will appear in a list with several other modules.
Description
Type a description of the module. This will help you know what it does.
Result File
Type the path to the directory where you want the execution results (a .log file) to be saved. The file is saved in: RACM Identity/logs.
Error File
Type the path to the directory where you want the error file (a .log file) to be saved. The file is saved in: RACM Identity/logs.
Behavior in case of errors
Select the way you want RAC/M to respond when an importation error occurs.
- b) Under Primitive:
Name
In the list, select the basic segment of code that the module needs to use to perform its task. >For a list of these segments (or primitives), refer to the *Technical Reference Guide
- c) Under Scope:
Criteria Column
Type the column heading you want to use as a filter.
Operation
Type “=” if you want the filter to equal a specific value.
Value
Type the value of the filter. If you type some text (or a string), make sure to use single quotation around it (for example, ‘Nurse’). You can use the SQL query format to use more advanced values.
- d) Under Table Selection:
Target Table
In the list, select the Identity and access repository table into which you want to import the data from the staging table. If you are using the module to manipulate data without necessarily importing it into the repository (for example, finding accounts that cannot be trusted), leave this list empty. In this case, the data mapping section will not appear.
Source Table
In the list, select the staging table from which you want to import the data. If you are using the module to perform normalization or correlation tasks, the source file will be a table located in the RAC/M repository.
Load Columns Headings from Tables
If you are ready to import the data, click this button to load the columns from the staging table to the RAC/M table. The data table opens under DATA MAPPING. Use the table to map data; if no mapping is needed, scroll down to the bottom of the page and click Save.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Target Table Column | These values represent the column headings of the RAC/M table. |
| Source Table Column | In this list you find all the columns of the data in the staging table. For each value on the Target Table Column select the item in the list that you want to correspond to that target value. |
| Data Type | In the list, select Date if the value is a date and String for another value. |
| Format | Type the format if necessary, if not, leave the box empty. For example, a date could have the yyyy-mm-dd string. |
| Treatment Type | In the list, select SRC_EMPTY_OVERIDE_BY_NULL if the value is empty and TARGET_IS_NOT_EMPTY_THEN_NO_OVERIDE if you do not want to override the value of the target. |
| Unique | Select this check box if the value must be unique. |
Example
An identification module could be configured as follows:
- On the Menu Bar, click CONFIGURATION> Modules.
- Click the
button. The module configuration page opens
- Under Details type the required information.
- Under Primitive, in the Name list, select ModuleCopyColumnsAndInsert.
- Under Table Selection, in the Target Table list, select Identification.
- In the Source Table list, select Identity_Import.
- Click Load Column Headings from Tables. The Data Mapping zone opens.
- In the Source Table Column list, next to Employee_ID, select Employee_ID.
- In the Data Type list, select String.
- Map the next Target Table Column entry and so on until all values are mapped.
- Click Save.
The module is created and added to the module list.
Configuring a Block
Blocks are made up of components, which can be formatters, collectors, or modules. When these components are put together to perform a task, they become blocks.
Example
If the information in an Excel spreadsheet needs to be added to the Identity and Access repository, you can create a block that would contain a formatter (to convert the Excel spreadsheet into a CSV format), a collector (to transfer the data from the CSV file into a RAC/M staging table), and a personalized module (to standardize the data).
When more elaborate tasks need to be executed, blocks can be grouped to form sequences.
To configure a block:
On the CONFIGURATION menu, click Blocks.
At the top right of the page, click the
button.
Under Details, in the Name text box, type the name you want to give to the block. The name should be distinctive as it will appear in a list with several other blocks.
In the Description text box, type a description of the block. This will help you know what it does.
Under Selected components, click a component on the left to select it and click the
button to add it to your block.
When a component is selected, its description opens to the right of the page. (When many components are selected, only the description of the first one is displayed.) To select many components in a same group, use the Ctrl key.

Once you have added all the needed components in the Selected Components list, click the Save button to create the block and add it to the list of available blocks. Subsequent changes will be saved by clicking the Update button.
You can keep working on your block by adding, deleting, and editing components:
To move the components up and down the Selected Components list, use the  and
and buttons. This determines the order in which the components are executed.
To temporarily disable a specific component, select the component and select the Disable check box.
To modify a component, select the component and click the button. The corresponding Configuration page opens.
Note
You can create a completely new component by clicking the button. This opens an empty configuration page for the corresponding component type. It is the same as going through the CONFIGURATION menu, component and clicking the
button at the top of the page.
Configuring a Sequence
Sequences are a collection of blocks that are executed in order to accomplish a process.
To configure a sequence:
- On the CONFIGURATION menu, click Sequences.
- At the top right of the page, click the
button.
- Under Details, in the Name text box, type the name you want to give to the sequence. The name should be distinctive as it will appear in a list with several other sequences.
- In the Description text box, type a description of the sequence. This will help you know what it does.
- In the Notification E-mails(s) and Failure E-mails(s) text boxes, type the email addresses of the identities that need to be notified when the sequence has been executed and the ones to be notified if an error occurs during the execution of a sequence.
- In the Schedule text box, type the scheduling string. The string includes 6 required fields and 1 optional one. Each field is separated by a white space.
| Field | Allowed Values | Allowed Special Characters |
|---|---|---|
| Seconds | 0-59 | , - * / |
| Minutes | 0-59 | , - * / |
| Hours | 0-23 | , - * / |
| Day of the month | 1-31 | , - * ? / L W |
| Month | 1-12 or JAN-DEC | , - * / |
| Day of the week | 1-7 or SUN-SAT | , - * ? / L ## |
| Year (Optional) | Empty, 1970-2199 | , - * / |
- * (asterisk) specifies all values. For example, in the Minutes field it means “every minute”.
- ? (question mark) is used for the Day of the month and Day of the week fields. It indicates “no specific value”, which is useful when you need to specify something in one of the two fields and not in the other.
- - (hyphen) specifies a range. For example, 10-12 in the Hours field means the hours 10 through 12 included.
- , (comma) specifies additional values. For example, in the Day of the week field, MON,WED,FRI means the days Monday, Wednesday, and Friday are scheduled.
- / (slash) specifies the increment. For example, in the Seconds field, 0/15 means the sequence will be executed every 0, 15, 30, and 45 seconds; if 5/15 then it will be every 5, 20, 35, and 50.”
- L (for last) has a different meaning in each of the two fields in which it is allowed. For example, in the Day of the month field it means the last day of the month. However, in the Day of the week field, by itself, it means 7 or SAT. But in the Day of the week field after another value, it means the last day of the month (For example 6L means the last Friday of the month; Saturday being 7).
- W (for weekday) specifies the weekday (Monday through Friday) nearest the given day. For example, if you specify 15W for the Day of the month field, this will mean “the nearest weekday to the 15th of the month". So if the 15th is a Saturday, the trigger will be Friday the 14th. If the 15th is a Sunday, the trigger will be Monday the 16th. If the 15th is a Tuesday, then it will be Tuesday the 15th. However if you specify 1W in the Day of the month, field and the 1st is a Saturday, the trigger will be Monday the 3rd; it will not ‘jump’ from one month to the next.
- ## (pound or hash) specifies the "n"th "dd" day of the month. For example, in the Day of the week field 6##3 means “the third Friday of the month” (day 6 being Friday and ##3 = the 3rd one in the month).
Under Blocks, click a block on the left to select it and click the
button to add it to your sequence.
When a block is selected, its description opens to the right of the page. (When many components are selected, only the description of the first one is displayed.) To select many components in a same group, use the Ctrl key.

Once you have added all the needed components in the Selected Components list, click the Save button to create the block and add it to the list of available blocks. Subsequent changes will be saved by clicking the Update button.
You can keep working on your sequence by adding, deleting, and editing blocks:
To move the blocks up and down the Selected Components list, use the  and
and buttons. This determines the order in which the blocks are executed.
To temporarily disable a sequence, under Details select the Disable the Sequence check box.
To modify a block, select the block and click the button. The corresponding Configuration page opens.
Note
You can create a completely new block by clicking the button. This opens an empty configuration page. It is the same as going through the CONFIGURATION> Blocks lock and clicking the
button at the top of the page.
Example
A sequence to import and copy data every Saturday at midnight could be configured as follows:
- On the CONFIGURATION menu, click Sequences.
- At the top right of the page, click the
button.
- Under Details, in the Name and Description text boxes, type the name and a description of the sequence.
- Under Blocks select the blocks you have created to copy and import data.
- In the Selected blocks list, use the
 and
and buttons to make sure that the importing block is executed before the copying block.
- In the Schedule text box, type 0 0 0 ? * 7 string.
- At the bottom of the page click Save or Update.
The sequence is created and will run at the scheduled time.
Configuring Mappings
When data is initially imported into RAC/M, you have to match the source data and the RAC/M tables. This is particularly the case for statuses. An organization may have several account statuses, but RAC/M only has a few. You have to decide which RAC/M statuses reflect each of the organization’s status.
The Mappings page is used to add categories, tags, sources, and external attributes when the source data name is unclear or difficult to work with, or to create working groups to refer to at la latter time.
Important
All the choices on this page are optional except for Status. All identities' status must be matched within the RAC/M environment. Because this is necessary for many RAC/M operations.
The following is a description of the possibilities you have to map source and output data. On the Menu Bar, click CONFIGURATION> Mappings.
Titles
Titles are imported for people and identities. If you want the name of a title to be displayed differently, you have to change its output name.
In the Technical Name list, select the title for which you want a different output name. You can give it a description, but it is not necessary. Then type the new name in the Display Name text box. This is the name that will be used in RAC/M Identity.
Click Update.
Note
If for some reason, you need to create a completely new title, at the top right of the page, click the button. Fill the text boxes and click the Save button.
Account Status
Accounts statuses are imported for assets and accounts. However, organizations may have several account statuses, while RAC/M only has a few. You must therefore assign a RAC/M status to each of the organization’s status.
This needs to be done the very first time data is imported and whenever a new status is created by the organization.
In the Display Name list, select the status for which you want to assign a RAC/M one. You can give it a description, but it is not necessary.
The selection you make here will be become the identity RAC/M status

To see the original identity status, click PEOPLE> **Identities, and click the identity to open its Details page.

Then, in the Effective Name list, select the RAC/M status.
Click Update.
Note
If for some reason, you need to create a completely new status, at the top right of the page, click the button. Fill the text boxes and click the Save button. If this is the default status, select the Default Status check box.
Employment Type
Employment types are imported for people and identities. If you want the name of an employment type to be displayed differently, you must change its output name.
In the Display Name list, select the employment type for which you want to assign a RAC/M one. You can give it a description, but it is not necessary. Then type the new name in the Technical Name text box. This is the name that will be used in RAC/M Identity.
Note
If for some reason, you need to create a completely new employment type, at the top right of the page, click the button. Fill the text boxes and click the Save button.
Categories
Categories are used when creating and importing assets. They enable you to define the level of the system or application.
To change the description, in the Display Name list, select the category for which you want to change the description and, in the Description text box, type the new. Click Update.
If you need a new category, at the top right of the page, click the button. Fill the text boxes and click the Save button.
Tags
Tags are used to help you sort accounts. This is useful when matching accounts and identities, especially if the list of accounts is very long. Tags can also help you create work groups for identities with similar characteristics.
To add a tag to an account or a provisioning request, click the button located at the top right of the page. Select either Account or Provisioning Request and, in the Display name list, type or select a tag name. Type a description in the Description text box and click Save.
Sources
Sources are used in the Identity page. They enable you to identify the identity source used to create an identity.
The Mappings page allows you to link the source to a target system, when applicable, or to create new sources.
To link a source, in the Display Name list, select the name of the file source you want to link to a target system. In the Description text box, type a description. Then type the associated value from the imported data in the Technical Name text box.
If the data is imported via a connector, select it in the ICF Connector list.
Click Update.
If you need to create a new source, click the button located at the top right of the page and enter the source information and click the Save button.
Extended Attributes
Extended Attributes appear in various pages, which allow you to add attributes that will help you link the different objects to the right person.
To add an extended attribute, click the attribute tab and click the button located at the top right of the page.
In the Display Name text box, type the name of the attribute. In the Description text box, type a description then type a name in the Technical Name text box. This is the name that will be used in RAC/M Identity.
If this is to be a unique identification key, select the Is Unique Key check box. To allow modification of the attribute, select the Attribute can be modified text box.
Click Save.
The attribute is added to the Column Name list of mapping tables. I is also added to the object (tab at the top) details page.
Configuring an ICF Connector
Please refer to the ICF Connector guide for more information.
Configuring Policies
RAC/M has the ability to automatically create accounts for identities during provisioning. To do so you need to create 3 policies: password, account, and username.
Configuring Password Policies
These policies are specifically used to define how the password to a new account will be constructed.
To define password policies:
- On the Menu Bar, click CONFIGURATION> Password Policies.
- At the top right of the page, click the
button.
- Under Details, in the Name text box, type a name for the password policy.

- In the Description text box, type the description of the policy.
- Under Parameters, enter the information as follows;
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Length | Type the minimal length the password must be. |
| Digit Characters | Type the minimal number of digits the password must have. |
| Lowercase Characters | Type the minimal number of lowercase characters the password must have. |
| Non-alphanumeric Characters | Type the minimal number of non-alphanumeric characters (for example, ##, $, &) the password must have. |
| Uppercase Characters | Type the minimal number of uppercase characters the password must have. |
- Click Save.
Configuring Account Policies
These are global policies that are used to determine how provisioning requests will be conducted. These parameters are usually configured when you first start using RAC/M Identity for your organization or when integrating a new application.
These policies apply to all provisioning requests which you can review on the ACCESS > Provisioning Request page.
To define an account policy:
- On the Menu Bar, click the CONFIGURATION> Account Policies.
- At the top right of the page, click the
button.
- Under Policies, in the Name text box, type the name of the policy.
- In the Description text box, type a description.
- In the Database list, select either Config or Data. Config is if you need a policy for a configuration application and Data for a database.
- In the Table Name List, select the RAC/M table for which the policy will apply. The choices differ according to the selection made in the Database list.
- Click the Save button at the bottom of the page.
- Under Options, in the RAC/M ID text box, type the ID number generated by RAC/M to identify the asset for which you want to create an account. You can find the ID number on the ASSETs> Assets> asset name Details page under Object ID.
- Select one or more of the following parameters:
Override Group on Account Activation
The previous accesses will be replaced with the new ones upon account reactivation. However, the current ones will remain the same.Active Directory
Indicates that you are working with Active Directory. This is necessary for group assignment discovery.Override Group on Account Modification
The previous accesses will be replaced with the new ones upon account modification. - Under Configuration, in the Password Policy list, select the password you have defined in the Defining Password Policies section.
- Click Update.
Configuring Username Policies
These policies are specifically used to define how the username will be constructed.
To define username policies:
On the Menu Bar, click CONFIGURATIN> Username Policies.
Under **Policy Proceed as follows:
a) In the Name list, select the account for which you want to define username policies.
Refer to the Defining Account Policies section.
b) In the Source Table list, select the table from which the user data will be taken.
This is generally the
Application_Accounttable.c) In the Target Table list, select the table in which the username will be saved.
This is generally the
Application_Accounttable,
Click the Save button at the bottom of the page.
Under Target Table, enter the required information.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Source Column | In the list, select the column in the source that contains data you want to use to create the username. |
| Data Source | In the list, select the source type of each column. Constant: Mapping will use the value you specify in the Constant/Value text box. For example, the RAC/M HR_Work_Location_Name column could always be “Downtown Office”. Date: Mapping will use the date format you specify in the Format text box. The date is taken from the selection made in the Source Column list. Make sure that you match the date formats. For example, the Hire_Date_Str column could display the date that was entered in the “Hire date” column of the source file. Cur_User: Mapping will use the user you specify in the Constant/Value text box. Column: Mapping will use the selection made in the Source Column list. For example, the RAC/M HR_Empl_Status_ID column could take its value from the Status column in the source file. Column_with_Default: Mapping will use the content directly from the source (column, file, or connector). If nothing is found, the value in the Constant/Value text box is used instead. Cur_Time: Mapping will use the current time as the value. File_Name: Mapping will use the name of the source file as the value. Column-Hashed: The value is hashed to fit the space allowed in the table. Column_Mask: Part of the value is masked using an expression defined in the Constant text box. For example, for a source value of 00430022887, you will obtain *******2887 if you use the following mask: ^d(7)[a-zA-Z0-9] or 0043002**** if you use: [a-zA-Z0-9].{3}$. |
| Target Column | In the list, select the column in which the username will be created. This is generally Account_Name. |
| Value | If the data source is Constant, type the value of the constant in this text box. |
| Number of Char | Type the number of characters (starting from the beginning) you want to use from the source columns. For example, you could use the first two letters of the first name. |
| Regex | This text box allows you to use a more advanced syntax in the Regular Expression format. |
| Add User ID Policy button | Click this button to add a new policy. |
| These buttons move the policies up or down. Policies are applied one after the other from the top down. |
User ID Collision Policy
If you think that certain username may end up being the same (for example, if you are using the first two letters of the first name and the first two letters of the last name along with a number), you can create collision policies to change the added number. To do so, select the Display user ID collision section check box.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Type a name for the collision policy. |
| Description | Type a description. |
| Use Sequential Value | Select this check box if you want the number added at the end of the username to increase sequentially. |
| Start value | Type the number with which you want to start. |
| Maximum value | Type the maximum value the usernames can reach. If there is no maximum value, select *Infinite. |
| Minimum Number of Digits | Type the minimum number of digits the number should have. For example, if you enter 0, the number will increase as 1, 2, 3, etc. If you enter 2, the number will increase as 01, 02, 03, etc. |
- Click the Update button.
Example
The following is an example of a username policy definition.
- Select the account for which you want to define username policies.
- In the Source Table and Target Table lists, select Application_Account.

Under Target Table in the Source Column list, select First_Name.
In the Data Source list, select Column.
In the Target Column list, select Account_Name.
In the Number of Char text box, type 2. The first two characters of the first name will be used.
Click Add User ID Policy.
a) In the Source Column, select Last_Name.
b) In the Data Source list, select Column.
c) In the Target Column list, select Account_Name.
d) In the Number of Char text box, type 2.
The first two characters of the last name will be used.
Click Add User ID Policy.
a) In the Source Column, select Account_Name.
b) In the Data Source list, select Constant.
c) In the Target Column list, select Account_Name.
d) In the Number of Char text box, type 01.
The username will end with "01”. Thus, if the person’s name is “John Smith”, his username would be “josm01”.
Select the Display user ID collision section check box.
- a) In the Name and Description text boxes, type the required information.
- b) Select Use Sequential Value.
- c) In the Start Value text box, type 1.
- d) In the Maximum Value text box, type 99.
- e) In the Minimum Number of Digits text box, type 2.
Click the Update button.
Consolidated provisioning emails
Emails that are sent when a provisioning request is processed are consolidated. This reduces the number of emails received by users.
Consolidation is done by recipient and by request target. In other words, each consolidated email contains all provisioning requests for a given recipient and target.
For example, if the same user makes several requests to add and remove access for the same identity, they will receive an email containing information on all these requests and, depending on the configuration in place, an email containing the passwords. Similarly, the target of these requests will receive a consolidated email containing information on all requests concerning them.
If a user makes several requests for different identities, they will receive one email per target identity, each containing information on all requests for that identity. As for the targets of these requests, they will receive a consolidated email containing all the accesses that concern them.
The same applies to all recipients of a provisioning request, i.e. the requester, the target, the target's supervisor and the members of the notification group.
Please refer to Provisioning notification for more information on configuring these notifications.
Sending logic configuration
When a provisioning request is processed, notifications are added to the queue.
An automated task regularly checks (depending on the mail.consolidation.job.quartz parameter) the queue and sends consolidated emails at the appropriate time, depending on the configuration in place.
As long as notifications are regularly created for the same recipient, they are not sent. This avoids sending consolidated emails before all requests have been processed.
The task detects whether notifications have recently been added to the queue (this is the mail.consolidation.min.delay.seconds parameter). If so, it does not send an email to this recipient. If no notification has been added to the queue since this time, the task sends a consolidated email for this recipient.
To prevent notifications from accumulating indefinitely in the queue without being sent, the task also checks whether the oldest notification for a recipient has existed for more than a certain time (this is the mail.consolidation.max.delay.seconds parameter). This could happen, for example, when processing a very large number of requests. If this is the case, it sends the consolidated emails to this recipient.
Four parameters can be used to configure the sending logic:
| Parameter | Description | Example values |
|---|---|---|
mail.consolidation.job.enabled | Enable or disable email sending functionality (if disabled, no email is sent) | true (enabled) or false (disabled) |
mail.consolidation.min.delay.seconds | Minimum time period before consolidated emails are sent for a recipient, in seconds | 300 (After 5 minutes) |
mail.consolidation.job.seconds | Maximum time period before sending consolidated emails for a recipient, in seconds | 3600 (After 1 hour) |
mail.consolidation.job.quartz | Time interval between job executions, in Quartz Scheduler format | 0 */5 * ? * * * (every 5 minutes) |
Retrying email delivery
In case of a failed email delivery, RAC/M Identity can retry sending the email in the future.
This feature can be configured in the configuration file using the following three parameters:
| Parameter | Description | Example values |
|---|---|---|
mail.retry.enabled | Enable or disable the feature | true (enabled) or false (disabled) |
mail.retry.interval.quartz | Time interval between retries, in the Quartz Scheduler format | 0 */5 * ? * * * (every 5 minutes) |
mail.retry.period.minutes | Maximum time period before giving up on delivery, in minutes | 10080 (After 1 week) |
Locale configuration
Overview
The locale configuration allows you to customize the appearance of RAC/M Identity according to the language and region of your users and/or your organization. It is used to display dates and times, as well as for emails sent to users.
A locale is a combination of language and region. For example, en_US is American English and fr_CA is Canadian French.
Global configuration
The application's default language and locale are configured in the conf/config.properties file via the default.system.language parameter. It defines the application's default language when no language is specified for a user. It can be a language (en) or a locale (en_CA), but using a locale is preferable for better precision.
Setting the locale for a specific language
You can specify a default locale for users whose region is not indicated in their profile. For example, some users have en as their language, without specifying the locale. To do this, simply add default.locale.en as a parameter for English and default.locale.fr for French.
For example, default.locale.en=en_US specifies that the default locale for users whose language is English is American English. By default, the locale used is en_CA (Canadian English) for English and fr_CA (Canadian French) for French.
This parameter also specifies the date format to be used in the interface for French and English.
Configuration by identity (emails only)
You can configure the language and locale of identities to customize the language and display of dates in emails sent to them. For example, an identity whose locale is en_UK will receive emails in English, and dates will be displayed in the British format.
Identities whose language is not specified receive emails in the default language defined via the default.system.language parameter. Similarly, dates are displayed in the default locale format.
Using the browser locale
It is possible to use the user's browser locale rather than the application's locale to display dates in the user interface. To do this, simply add override.browser.locale.for.dates=false to conf/config.properties.
